Mindmaps are powerful tools that can transform the way healthcare professionals organize information, develop treatment plans, and collaborate with colleagues. In a field where clarity, efficiency, and innovation are paramount, mindmaps provide an intuitive and visual method for enhancing various aspects of healthcare. This blog will explore five amazing ways to incorporate mindmaps into healthcare settings, offering practical guidance on how to maximize their potential.
Patient-Focused Strategies

Image from: QianKuWang
1. Improving Patient Education and Communication
- Why Mindmaps Are a Powerful Tool for Patient Communication
Effective communication with patients is absolutely essential for ensuring they have a clear understanding of their condition, treatment options, and the specific steps they need to take for a successful recovery. Traditional methods of conveying medical information, often laden with technical jargon, can be overwhelming for patients and may result in confusion or misinterpretation. Mindmaps provide a simplified, visual alternative that breaks down complex medical information into smaller, more manageable pieces. This visual approach not only makes the information more accessiblebut also allows patients to see the connections between different aspects of their health. By using mindmaps, healthcare providers can ensure that patients are better informed, which in turn can lead to greater patient engagement, improved adherence to treatment plans, and ultimately, better health outcomes.
- How to Create Patient-Friendly Mindmaps
- Central Concept: Begin by placing the central concept, such as the diagnosis or primary treatment goal, at the center of the mindmap. This central node acts as the foundation upon which all other information will be built, ensuring that the patient’s main concern is clearly identified.
- Branch Out Key Areas: From this central concept, branch out into key areas relevant to the patient’s condition, such as symptoms, causes, treatment options, and lifestyle changes. Each of these branches should represent a critical component of the patient’s care, helping to structure the information in a way that is logical and easy to follow.
- Use Simple Language: Throughout the mindmap, make sure to use simple and clear language, avoiding medical jargon that could confuse the patient. The goal is to make the information as easy to understand as possible, ensuring that patients can follow the discussion without feeling overwhelmed.
- Incorporate Visual Elements: Where appropriate, incorporate images or icons to represent different aspects of the mindmap. For example, you might use a heart icon to represent cardiovascular health or a pill icon to symbolize medication. These visual elements can make the information more engaging and memorable for the patient.
- Encourage Patient Engagement: By breaking down the information into a clear and visual format, mindmaps can encourage patients to ask questions and actively participate in their care. Providing a mindmap, either in print or digitally, allows patients to revisit the information whenever needed, reinforcing their understanding and helping them stay informed about their health.
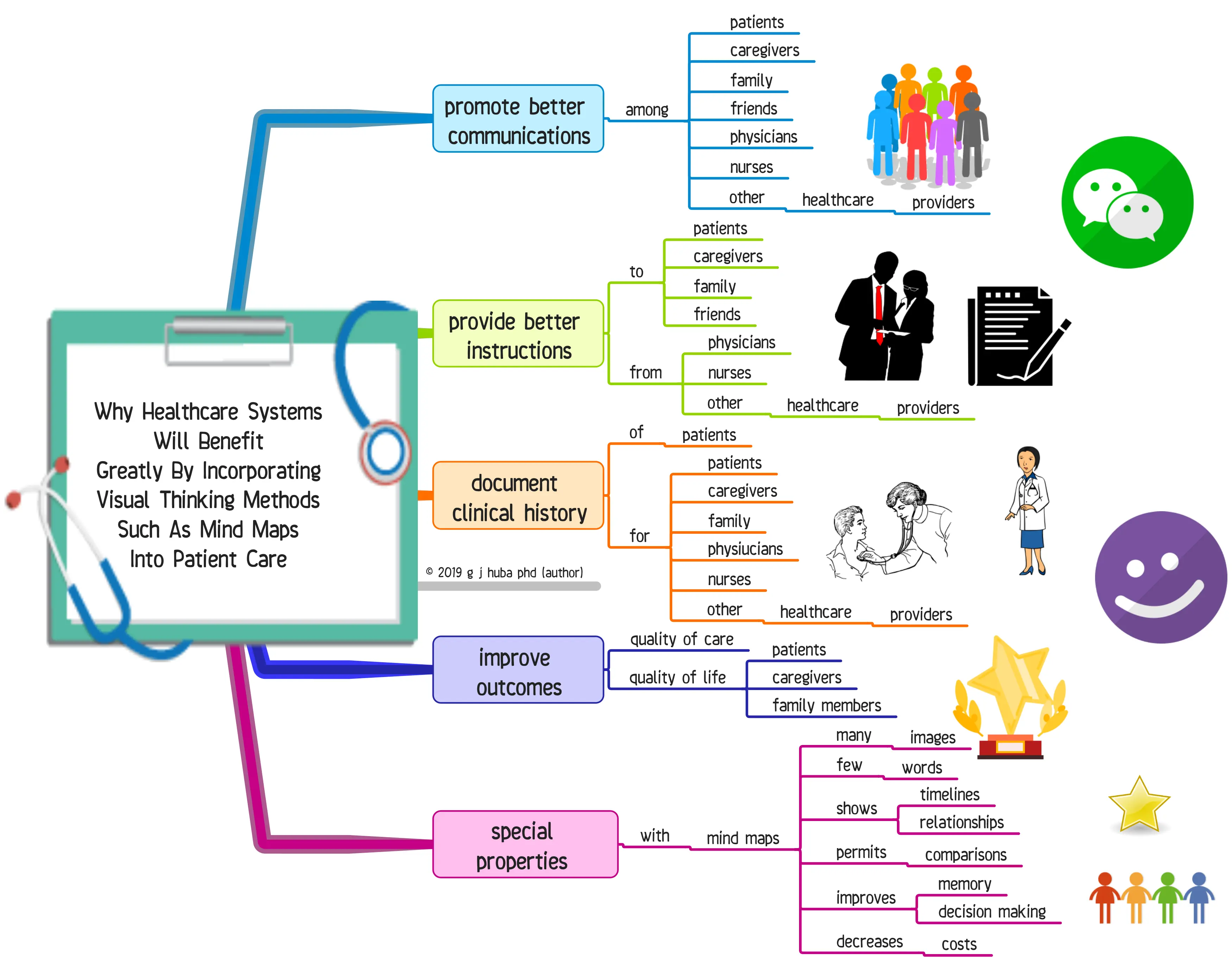
Image from: Hubaisms
2. Enhancing Patient Care Plans
- Why Use Mindmaps for Care Plans
Traditional care plans often follow a linear and restrictive format, which can make it challenging to capture the full complexity of a patient’s needs. In many cases, these plans may not fully reflect the intricate connections between different aspects of a patient’s health, leading to gaps in care or a lack of personalized attention. Mindmaps offer a dynamic and flexible alternative that allows healthcare professionals to visualize and organize the various components of a care plan in a more comprehensive and interconnected way. By using mindmaps, healthcare providers can easily incorporate and visualize a wide range of information, such as diagnosis, treatment options, patient preferences, lifestyle factors, and follow-up schedules. This approach not only makes the care plan more comprehensive but also enhances its adaptability, ensuring it can be easily updated as the patient’s condition evolves or as new information becomes available. The visual structure of mindmaps helps healthcare teams identify relationships and potential gaps in care, fostering a more holistic approach to patient management.
- How to Create an Effective Care Plan Mindmap
- Centralize the Patient’s Identity: Start by placing the patient’s name or case number at the center of the mind map. This central node serves as the foundation of the care plan, ensuring that the entire map is focused on the patient’s individual needs and circumstances.
- Branch Out Key Areas: From the central node, branch out into key areas such as medical history, current symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and patient goals. These branches represent the core components of the care plan, providing a structured overview of the patient’s health status and the primary areas of focus.
- Detail Each Branch: Each of these key areas can be further expanded into more detailed sub-nodes. For example, under-treatment options, include branches for specific medications, therapies, or lifestyle changes. Under patient goals, include sub-nodes for short-term and long-term objectives, as well as any personal preferences or concerns that the patient may have. This level of detail ensures that the care plan is both comprehensive and tailored to the patient’s unique situation.
- Incorporate Patient Preferences and Goals: A significant advantage of using mindmaps is the ease with which patient preferences and goals can be incorporated. Include notes that capture the patient’s input on treatment choices, lifestyle adjustments, and desired outcomes. This personalized approach ensures that the care plan is aligned with what matters most to the patient, which can improve adherence and satisfaction.
- Ensure Adaptability and Flexibility: The visual and flexible nature of mindmaps makes them ideal for adapting to changes in the patient’s condition or treatment response. As new information becomes available or as the patient’s needs evolve, the mindmap can be easily updated, ensuring that the care plan remains relevant and effective over time.

Image from: Medium
Healthcare Provider-Focused Strategies

Image from: TuGuaiShou
3. Streamlining Multidisciplinary Team Meetings
- Why Mindmaps Are Perfect for Team Collaboration
In healthcare, collaboration among various disciplines is essential for delivering the best possible patient outcomes. Multidisciplinary team (MDT) meetings are a cornerstone of this collaborative approach, bringing together specialists from different fields to discuss and plan patient care. However, these meetings can sometimes become disorganized, with critical details getting lost in lengthy discussions or miscommunication among team members. Mindmaps provide an ideal solution by offering a clear visual structure that keeps the conversation focused and ensures that all relevant information is captured and organized effectively. By using mindmaps, MDT meetings can be transformed into more efficient and productive sessions where each specialist’s input is clearly documented and easily accessible. This not only improves the quality of the decision-making process but also ensures that all team members are on the same page, leading to more coordinated and effective patient care.
- How to Use Mindmaps in MDT Meetings
- Create a Centralized Mindmap: Before the meeting, the team leader should create a mindmap with the patient’s case at the center. This central node serves as the focal point for all discussions and ensures that the meeting remains centered on the patient’s specific needs and condition.
- Branch Out to Represent Specialists: From the central node, branch out to represent the different specialists involved in the patient’s care, such as surgeons, nurses, physiotherapists, and social workers. Each branch corresponds to a specialist’s area of expertise, providing a structured way to organize their input.
- Detail Each Specialist’s Contributions: Under each specialist’s branch, include sub-nodes that detail their contributions, observations, and recommendations. This could include notes on specific treatments, diagnostic results, patient interactions, or concerns that the specialist may have. By capturing this information in the mindmap, the team can ensure that no important detail is overlooked.
- Real-Time Updates During the Meeting: During the meeting, the mindmap can be projected onto a screen and updated in real-time as discussions progress. This allows all team members to see how their contributions fit into the overall care plan and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
- Share and Use as a Reference: After the meeting, the completed mindmap can be shared with all team members as a reference for future discussions and actions. This shared document serves as a living record of the meeting, providing a clear and organized overview of the patient’s care plan and facilitating better communication and coordination among the team.
4. Facilitating Medical Research and Data Analysis
- Why Mindmaps Are Ideal for Research
Medical research is often a complex and intricate process that involves sifting through vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and generating new hypotheses. The traditional methods of organizing research data, such as spreadsheets or text documents, can be cumbersome and may not effectively highlight the relationships between different pieces of information. Mindmaps provide an ideal solution by offering a flexible and visual way to organize research findings. This approach allows researchers to see the big picture more clearly, making it easier to identify connections, relationships, and trends within the data. Additionally, mindmaps can help researchers organize their thoughts, track their progress, and ensure that no important aspect of the research is overlooked. By using mindmaps, researchers can more efficiently navigate the complexities of their studies, leading to more coherent and insightful conclusions.
- How to Use Mindmaps for Research
- Centralize the Research Focus: Begin by placing the main research question or hypothesis at the center of the mindmap. This central node serves as the foundation of the mindmap, ensuring that all subsequent information is directly related to the primary focus of the research.
- Branch Out Key Areas: From the central node, branch out into key areas that are essential to the research process, such as literature review, data collection methods, findings, and implications. Each of these branches represents a critical component of the research, helping to structure the process in a logical and organized manner.
- Expand Each Branch with Detailed Nodes: Under each key area, include detailed nodes that capture specific studies, data points, observations, or methodologies. For example, within the literature review branch, you could create nodes for each key study or paper that is relevant to your research. This level of detail ensures that all important information is captured and easily accessible.
- Identify Relationships and Trends: The visual nature of mindmaps makes it easier to identify relationships and trends within the data. By connecting related nodes or highlighting key patterns, researchers can develop a more nuanced understanding of the research findings and generate new insights or hypotheses.
- Present and Share Findings: Once the mindmap is complete, it can be used to present the research findings in a clear and concise manner. Whether in a written report or during a presentation, the mindmap provides a visual overview that helps colleagues, stakeholders, or peers quickly grasp the key points and significance of the research.
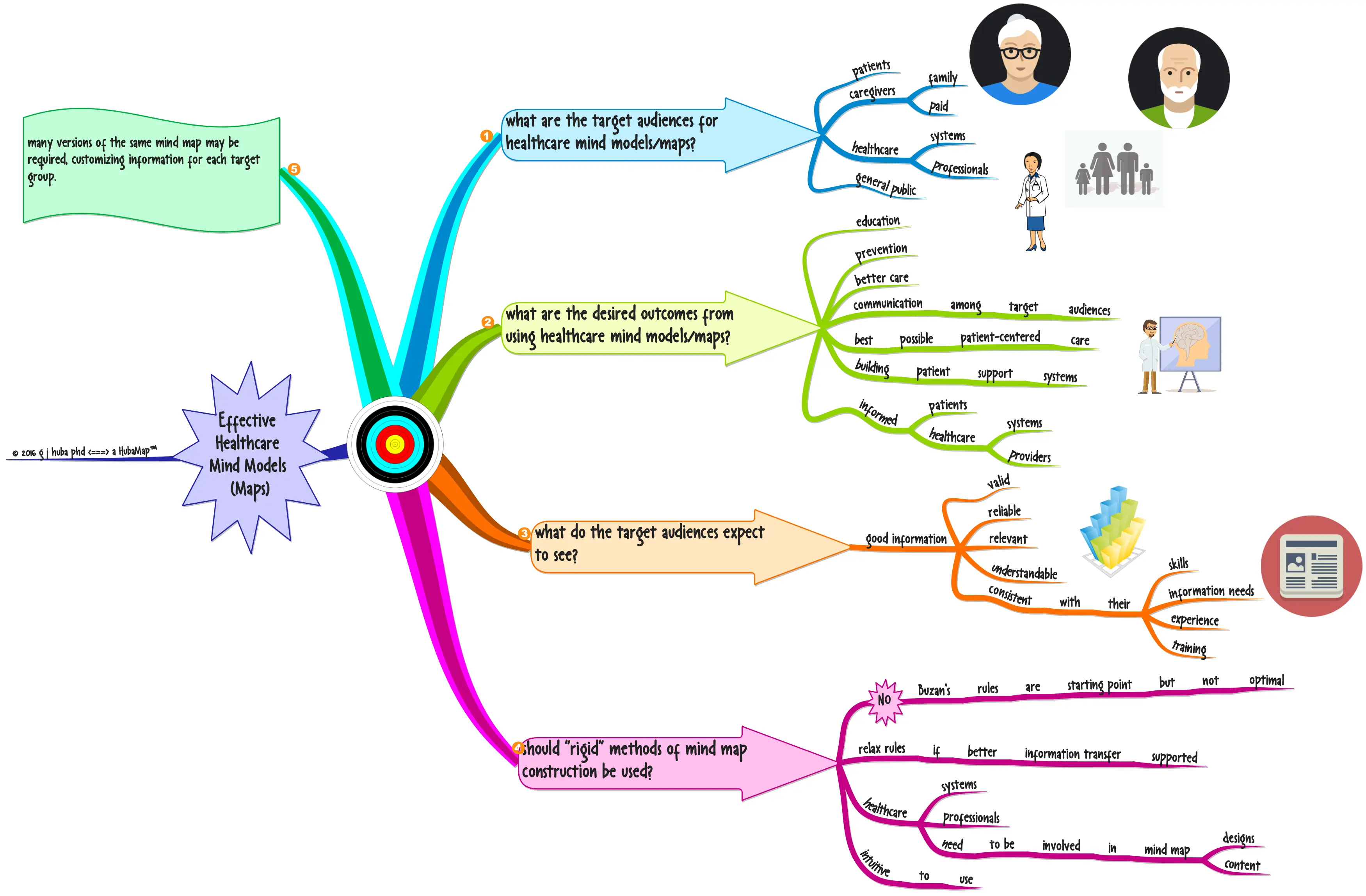
Image from: Hubaisms
5. Optimizing Administrative and Workflow Processes
- Why Mindmaps Are a Game-Changer for Healthcare Administration
Healthcare facilities are inherently complex organizations that require the efficient management of numerous administrative tasks and workflows. From scheduling and resource allocation to policy development and quality assurance, there are countless processes that need to be carefully coordinated to ensure the smooth operation of the facility. Traditional methods of managing these tasks, such as lists or spreadsheets, can often be overwhelming and difficult to navigate. This is where mindmaps come into play as a powerful tool that can help administrators visualize and optimize these processes. By providing a clear, visual representation of tasks, timelines, and responsibilities, mindmaps enable administrators to see the big picture while also focusing on the finer details. This not only enhances efficiency but also ensures that all aspects of the organization’s operations are accounted for, leading to better coordination, transparency, and overall effectiveness.
- How to Implement Mindmaps in Administrative Tasks
- Identify the Primary Objective: Start by placing the central node of the mindmap to represent the primary objective of the task or process. For example, if the task is to develop a new policy, the central node could be labeled with the policy’s primary objective or goal. This ensures that all subsequent branches and nodes remain focused on achieving this central goal.
- Branch Out Key Areas: From the central node, branch out to include key areas that need to be considered in the process. For a policy development task, these branches could include legal considerations, staff training, patient impact, and cost analysis. Each of these branches represents a critical aspect of the task that needs to be addressed.
- Expand with Specific Tasks and Details: Under each key area, further expand the mindmap with specific tasks, deadlines, and responsible personnel. For instance, under staff training, you might include nodes for creating training materials, scheduling training sessions, and assigning trainers. This level of detail helps to ensure that all necessary tasks are identified and that there is a clear plan for how and when each task will be completed.
- Track Progress and Identify Bottlenecks: One of the key benefits of using mindmaps is the ability to track progress and identify potential bottlenecks in real-time. As the tasks are completed, the mindmap can be updated to reflect the current status, making it easier to see where delays or issues might arise. This proactive approach allows administrators to address challenges early, ensuring that the process stays on track.
- Streamline Workflow Processes: Beyond individual tasks, mindmaps can also be used to streamline entire workflows. By mapping out the steps involved in a particular process, such as patient intake or resource allocation, administrators can identify opportunities for improvement and make adjustments to optimize efficiency. This might include eliminating redundant steps, reallocating resources, or implementing new technologies.

Image from: Wondershare EdrawMind
Incorporating mindmaps into healthcare settings can lead to significant improvements in patient care, team collaboration, research, and administrative efficiency. Their ability to visually organize complex information makes them an invaluable tool for healthcare professionals looking to enhance their practice. Whether you’re developing a care plan, conducting research, or optimizing workflows, mindmaps offer a flexible and powerful solution that can lead to better outcomes for both patients and providers. By embracing these five amazing ways to use mindmaps, healthcare professionals can unlock new levels of clarity, efficiency, and innovation in their daily practice.