Brainstorming can face creative blocks, dominant voices overshadowing others, lack of structure causing scattered ideas, difficulty organizing numerous concepts, and challenges in remote collaboration. These issues hinder idea generation, equitable participation, focus, prioritization, and effective communication, reducing the session’s overall productivity and innovation.
In this case, mind mapping is a versatile and powerful tool for brainstorming, creative thinking and problem-solving in a visually structured way. By organizing ideas and concepts around a central theme, mind maps help in exploring, connecting, and refining thoughts. In this blog, we will explore effective techniques for using mind maps to boost creativity during brainstorming sessions.
Set Ground Rules
Before diving into the brainstorming process, it’s essential to establish some ground rules to ensure the session is productive and inclusive. Setting ground rules helps create a structured environment that encourages participation and maintains focus.
- Encourage Open-Mindedness: Ensure that all participants understand the importance of being open to all ideas, regardless of how unconventional or impractical they might seem initially. Creativity thrives when there is no judgment during the idea generation phase.
- Implement the “Yes, and…” Approach: Borrowed from improvisational theater, this technique involves building on each other’s ideas rather than shutting them down. When someone presents an idea, others should respond with “Yes, and…” to expand on it, creating a collaborative and positive atmosphere.
- Document Everything: Write down all ideas, not just the ones that seem feasible or practical. This prevents the premature dismissal of potentially valuable concepts and ensures that all contributions are considered.
- Equal Participation: Make sure everyone in the group contributes. This can be done by going around the room or using a collaborative tool that allows everyone to input their ideas anonymously if needed.
- Time Limits: Set specific time limits for each phase of the brainstorming session to keep the process moving and to maintain momentum. For example, allocate a fixed amount of time for idea generation before moving on to discussion and refinement.
These ground rules help to create a safe and structured environment where creativity can flourish. They also ensure that the brainstorming session stays focused and productive, allowing the team to generate a wide range of ideas efficiently.
Collaboration is a key component of effective brainstorming, and mind maps are particularly well-suited to collaborative sessions. Whether you’re working with a team in person or remotely, mind mapping tools can facilitate real-time collaboration and idea sharing.
- Use Digital Tools for Collaboration: Tools like MindMeister, Lucidchart, and Coggle allow team members to collaborate on mind maps in real-time. This is especially useful for remote teams, as it enables participants to contribute ideas simultaneously, regardless of location.
- Encourage Diverse Perspectives: In a collaborative session, make sure to involve participants from different backgrounds and areas of expertise. Diverse perspectives can lead to more creative solutions and help to identify potential issues that might be overlooked by a more homogenous group.
- Facilitate Open Communication: Ensure that everyone has the opportunity to contribute during the brainstorming session. Use the ground rules established earlier to create an environment where all voices are heard and respected.
Collaborative mind mapping not only enhances the quality of the brainstorming session but also fosters a sense of ownership and alignment within the team, leading to more effective implementation of ideas.
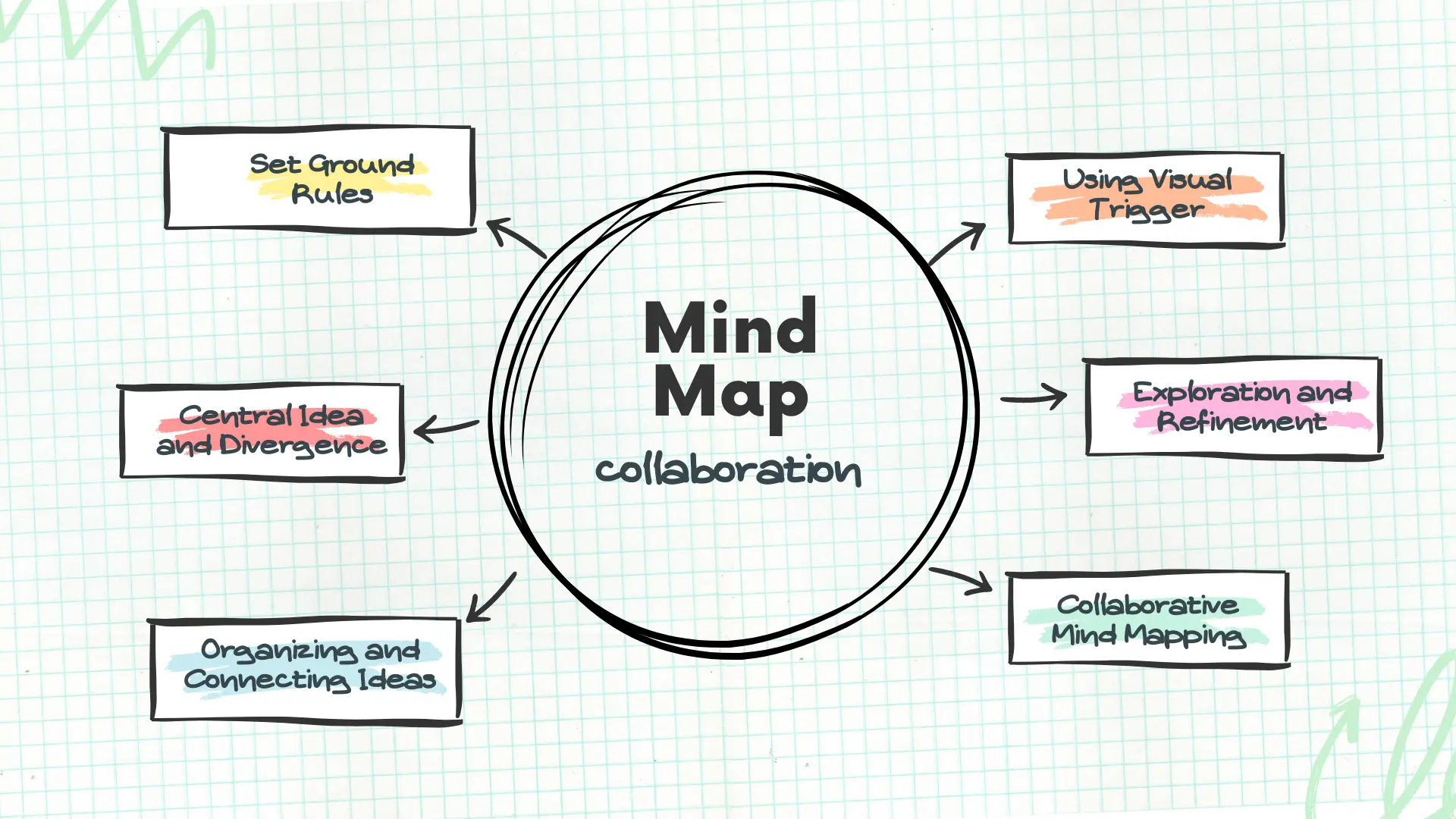
Central Idea and Divergence
The core of any mind map is the central idea or theme, from which all other thoughts and concepts radiate. This central node serves as the anchor for the entire brainstorming session, helping to keep the team focused on the main objective.
- Start with a Clear Central Theme: Begin by placing the main problem, topic, or goal at the center of the mind map. This could be a specific challenge, a project goal, or a general theme that needs exploration. The central theme should be clearly defined and concise, as it guides the direction of the brainstorming session.
- Encourage Divergent Thinking: Once the central theme is established, encourage participants to think broadly and generate as many ideas as possible. This phase is all about quantity over quality—participants should feel free to share any and all ideas, no matter how wild or unstructured they might be.
- Use Prompts to Spark Ideas: If the brainstorming session stalls, introduce prompts or questions to stimulate thinking. Questions like “What if?”, “How might we?”, or “What could go wrong?” can help break through creative blocks and encourage more diverse ideas.
By focusing on a central idea and promoting divergent thinking, mind maps allow teams to explore a wide range of possibilities, setting the stage for innovative solutions.
Exploration and Refinement
Once the initial ideas are generated and organized, the next step is to explore and refine them. This phase involves deepening the exploration of promising ideas, combining concepts, and narrowing down the options.
- Deepen Exploration: Take the time to explore the most promising ideas in greater detail. This might involve breaking down the ideas into smaller components, asking probing questions, or considering different perspectives.
- Combine Ideas: Look for opportunities to combine ideas to create more comprehensive solutions. Sometimes, two or more seemingly unrelated ideas can be merged to form a stronger, more innovative concept.
- Converge on the Best Solutions: After exploring and refining the ideas, it’s time to converge on the best solutions. Use criteria such as feasibility, impact, and alignment with goals to evaluate and select the top ideas for further development.
Exploration and refinement are crucial steps in turning raw ideas into actionable solutions. By taking the time to delve deeper and combine concepts, you can uncover innovative approaches that might not have been apparent initially.
Organizing and Connecting Ideas
After generating a broad range of ideas, the next step is to organize and connect them within the mind map. This phase involves grouping similar concepts, identifying patterns, and drawing connections between related ideas.
- Categorize Ideas: Begin by grouping related ideas together. In a mind map, this is done by creating branches from the central node and sub-branches from those main ideas. Each branch represents a category, helping to organize thoughts into coherent sections.
- Identify Patterns and Relationships: As ideas are categorized, look for patterns and relationships between them. Use lines or arrows to connect related concepts, showing how they influence or build on each other. This visual representation helps to clarify complex relationships and can reveal new insights.
- Prioritize and Refine: Once the ideas are organized, prioritize them based on their relevance and feasibility. Highlight the most promising concepts and refine them further, either by adding more details or by combining them with other ideas to create more robust solutions.
Organizing and connecting ideas within a mind map not only makes the brainstorming session more productive but also helps in visualizing the relationships between different concepts, leading to a deeper understanding of the problem at hand.
Using Visual Trigger
Visual triggers play a crucial role in enhancing creativity during mind mapping. By incorporating colors, images, and symbols, you can stimulate both the logical and creative sides of the brain, making the brainstorming session more engaging and effective.
- Use Colors to Differentiate Ideas: Colors can be used to distinguish between different categories or types of ideas within a mind map. For example, you might use one color for risks, another for opportunities, and yet another for resources. This makes the mind map more visually appealing and easier to navigate.
- Incorporate Images and Symbols: Adding images and symbols to your mind map can help in visualizing abstract concepts and making the ideas more memorable. For instance, an icon of a light bulb could represent innovative ideas, while a dollar sign could indicate financial considerations.
- Leverage Mind Mapping Software: Many digital mind mapping tools offer features that make it easy to integrate visual elements. Tools like MindMeister, Xmind, and Lucidchart allow you to drag and drop images, change colors, and add icons, enhancing the visual impact of your mind map.
Using visual triggers not only makes the mind map more engaging but also helps in triggering creative thoughts, making it easier to generate and organize ideas.
Summary
Mind mapping is a powerful technique for brainstorming and creative thinking, offering a structured yet flexible way to generate, organize, and refine ideas. By setting ground rules, focusing on a central idea, using visual triggers, and embracing collaboration, you can make your brainstorming sessions more productive and innovative. Whether you’re working alone or with a team, these techniques can help you unlock new possibilities and turn creative ideas into actionable solutions.





.pHGuAiTS_ZtVcxn.webp)