In today’s information-driven world, organizing data visually is key to enhancing comprehension and productivity. One effective tool for this is the tree mind map, a versatile diagram that helps structure complex ideas in a clear, hierarchical format. In this blog, we’ll explore the best practices for tree map design that can take your visualization skills to the next level.
A tree mind map is a diagram used to display data hierarchically, resembling a branching tree structure. Starting with a central node, it branches out into subtopics, forming a visual representation of ideas or information. Unlike traditional mind maps, tree mind maps are more structured and linear, making them ideal for hierarchical data, project planning, or decision trees.
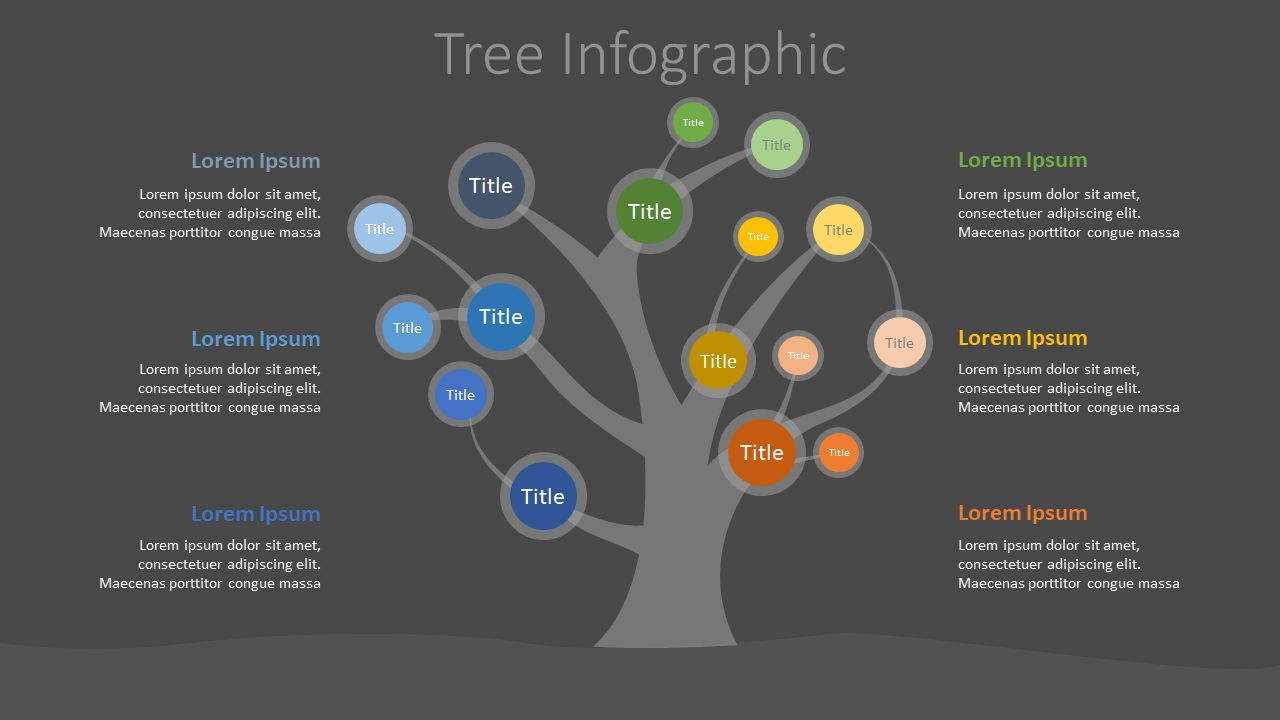
Image from:Powered template
Why Tree Maps Matter in Design
Tree mind maps are powerful tools that can greatly enhance the way we process, organize, and present information. Whether you’re managing a project, brainstorming ideas, or analyzing data, tree maps provide a visually intuitive method for structuring information. Here’s why they are particularly valuable in design:
In today’s data-rich environment, making sense of large amounts of information can be challenging. Tree mind maps excel at simplifying this complexity by breaking down large data sets into more manageable components. By categorizing and sub-categorizing information in a hierarchical structure, tree maps allow you to see the big picture while diving into specific details when needed. This approach makes it easier to identify relationships between different elements and provides clarity, especially in complex projects or problem-solving scenarios.
2. Enhance Learning and Memory
The human brain naturally organizes and stores information in patterns, making tree maps effective for learning. The hierarchical structure of tree mind maps mirrors how our brains process and recall information. By arranging concepts from general to specific, tree maps create logical connections that are easier to remember. Studies show that associating ideas with visual structures improves retention and recall. Tree maps not only help organize thoughts but also make it easier to retrieve key information when needed.

Image from:owlcation
3. Improve Decision-Making
Decision-making often involves evaluating multiple options, outcomes, and variables. Tree maps are effective in this context as they visually lay out choices in a clear, branching structure. This allows you to assess different pathways, compare pros and cons, and weigh risks versus rewards more efficiently. By mapping out decision trees or scenarios, you can trace consequences and potential outcomes, leading to more informed and confident decisions. Whether choosing between business strategies or evaluating different project plans, tree maps provide a structured framework for effective analysis.

Image from:venngage
4. Foster Better Communication and Collaboration
Tree mind maps are not just for individual thinking—they are also excellent communication tools. In team settings, they provide a shared visual language that makes complex ideas easier to discuss. The structured nature of tree maps reduces misunderstandings by clearly outlining relationships between concepts. During meetings or collaborative brainstorming sessions, tree maps help groups stay organized and focused, ensuring everyone is on the same page and that important details are not overlooked.
While tree maps are often linked to structured information, they are also powerful tools for creative thinking. By branching out ideas from a central theme, tree maps encourage expansive thinking. Each branch represents a new direction, helping explore various possibilities without losing sight of the original goal. This is especially useful in brainstorming sessions, where the tree map format helps generate and organize creative ideas in a logical manner.

Image from:oreilly
6. Increase Efficiency in Data Organization
Tree maps are widely used in organizing large volumes of data, especially in fields like software development, content management, and business analysis. By categorizing information into a well-defined hierarchy, tree maps reduce clutter and make it easier to access relevant data quickly. This organized data structure is particularly helpful in developing complex systems, managing content libraries, or tracking business processes.
Image from:mavink
Best Practices for Tree Map Design
When designing a tree mind map, following best practices is essential to ensure clarity, efficiency, and visual appeal. Here are some key tips:
1. Start with a Clear Central Theme
The root node or central idea is the foundation of your tree mind map. Ensure that this theme is both clear and concise to effectively set the direction for all the branches that follow. A well-defined central theme guides the flow of information, helping users to stay focused and maintain alignment with the core concept as they build out the map.
2. Use a Logical Structure
Follow a hierarchical arrangement where parent branches lead to more specific child branches. Organize related subtopics logically to maintain coherence and ensure that the information flows naturally from general to specific. This logical structure not only makes the map easier to understand but also helps in identifying relationships between different ideas, enabling a more comprehensive analysis.
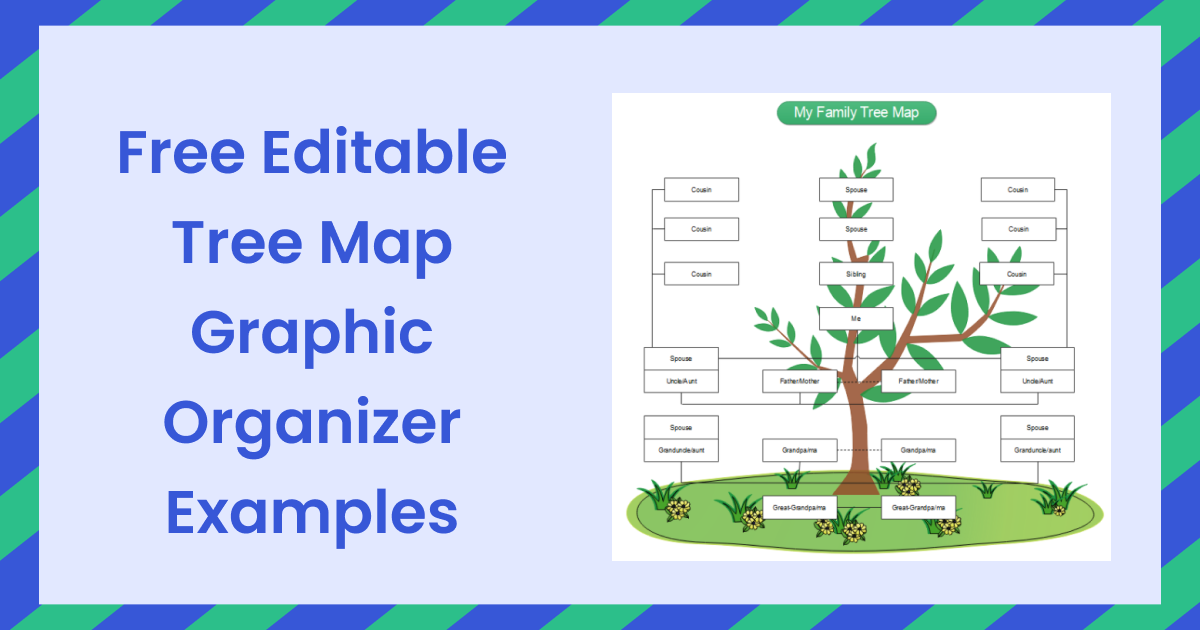
Image from:edrawmax
3. Prioritize Simplicity and Clarity
Avoid overcomplicating your tree mind map with too many branches or nodes. Aim for simplicity and clarity by keeping each branch focused on a single idea or category. A streamlined map allows users to quickly grasp the overall structure without becoming overwhelmed by excessive detail, making it more effective as a tool for both learning and communication.
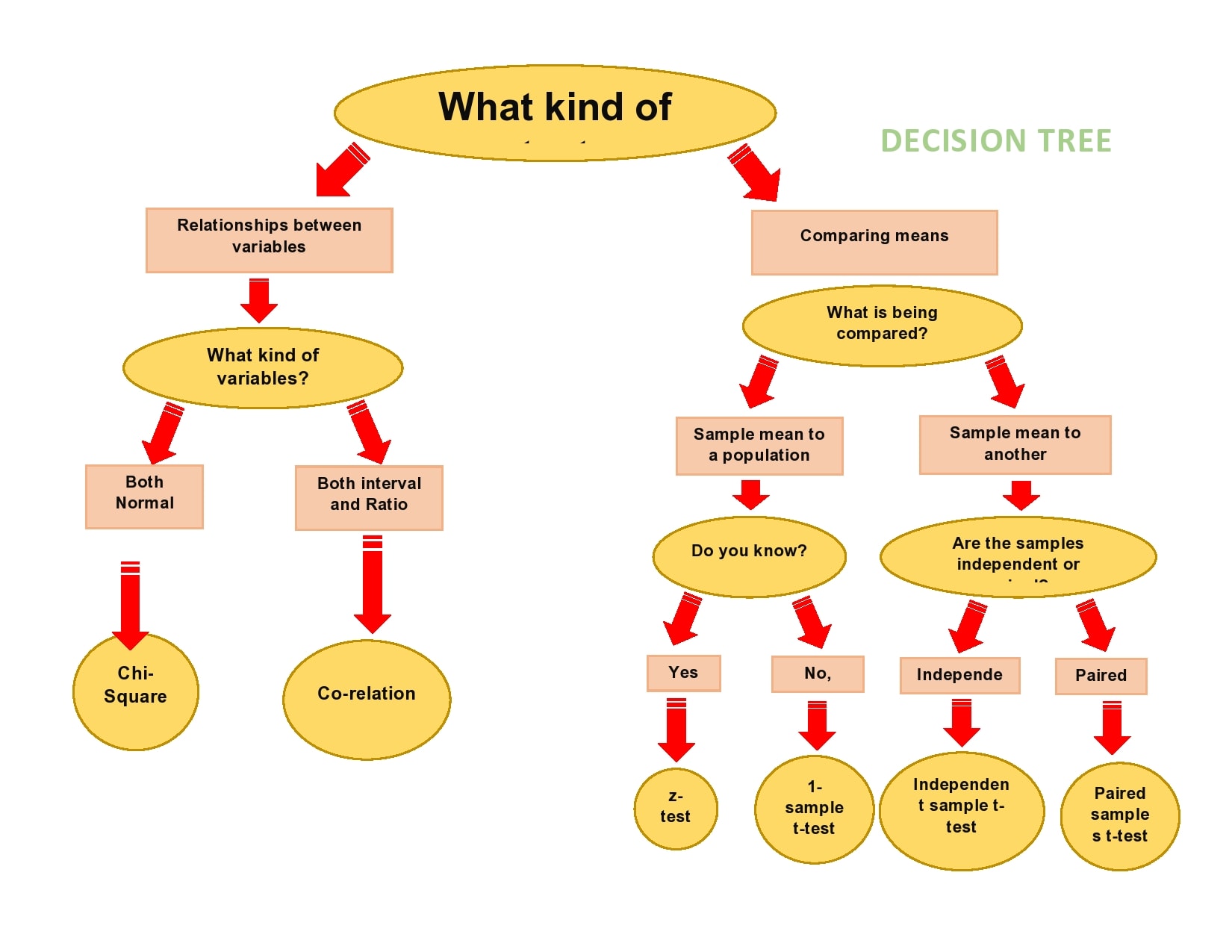
Image from:mungfali
4. Color-Code for Visual Distinction
Use color strategically to differentiate between branches and highlight key sections. Consistent color coding helps users quickly identify relationships between nodes and navigate the map more easily. By visually distinguishing different parts of the map, color-coding enhances comprehension and retention, making the information more memorable.
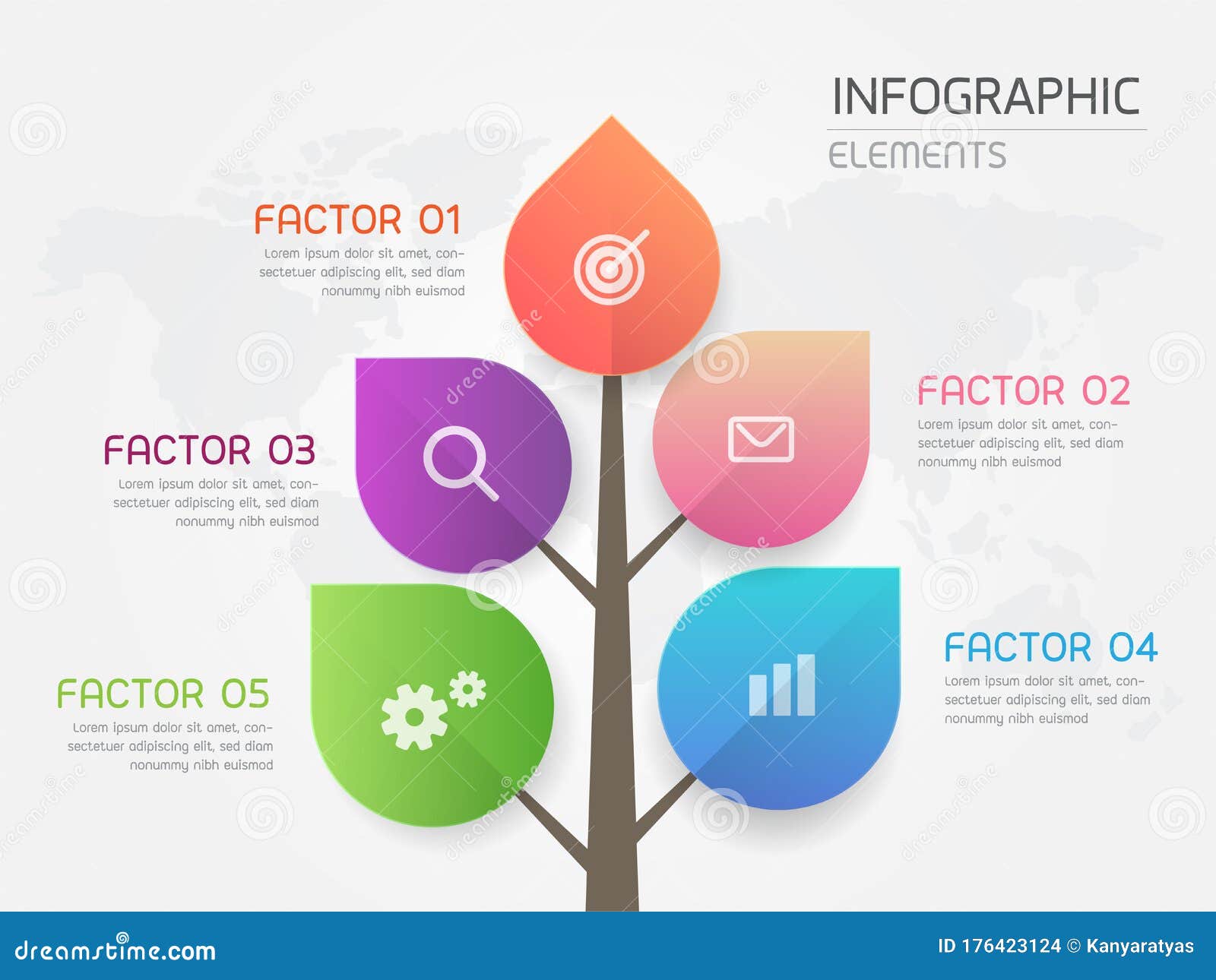
Image from:cartoon dealer
5. Maintain Balanced Spacing
Ensure that branches are evenly spaced, with sufficient gaps between different nodes. Crowded branches can create confusion and reduce the effectiveness of your map by making it difficult to distinguish between ideas. Balanced spacing enhances the visual appeal of the map and allows for easier navigation, ensuring that all components are clearly visible and accessible.
6. Limit Text Content
Each node should contain concise, relevant information. Avoid long blocks of text; instead, use keywords and short phrases to convey ideas. This approach not only keeps the map visually clean but also ensures that the information is quickly digestible, making it easier for users to focus on the key points without getting bogged down in unnecessary details.
7. Incorporate Icons and Visuals
Adding simple icons or visuals can make the tree mind map more engaging and easier to understand. Visual elements can serve as intuitive cues that reinforce the meaning of the text. However, avoid overwhelming the design with too many decorative elements, as this can detract from the clarity and purpose of the map. Use visuals sparingly and strategically to enhance rather than clutter the map.

Image from:colourbox
8. Use Consistent Line Styles
Keep line thickness and styles uniform throughout your map to maintain visual consistency. Consistent line styles help ensure that the hierarchy remains clear, with main branches distinctly separated from sub-branches. This uniformity not only enhances the visual appeal of the map but also makes it easier for users to follow the flow of information and understand the relationships between different nodes.
9. Test and Iterate
Share your tree mind map with others to gather feedback. Use this input to iterate and make adjustments that enhance the map’s clarity and effectiveness. Testing your map with a diverse audience can reveal areas of improvement that you might not have noticed, ensuring that the final product is as user-friendly and informative as possible.

Image from:Researchgate
Use Cases for Tree Mind Maps
Tree mind maps are versatile and can be used in various scenarios:
1. Project Planning:
Break down complex projects into actionable steps.

Image from:pinterest
2. Decision Trees:
Analyze different choices and their possible outcomes.

Image from: Biggerplate
3. Organizational Charts:
Display company structures and team hierarchies.
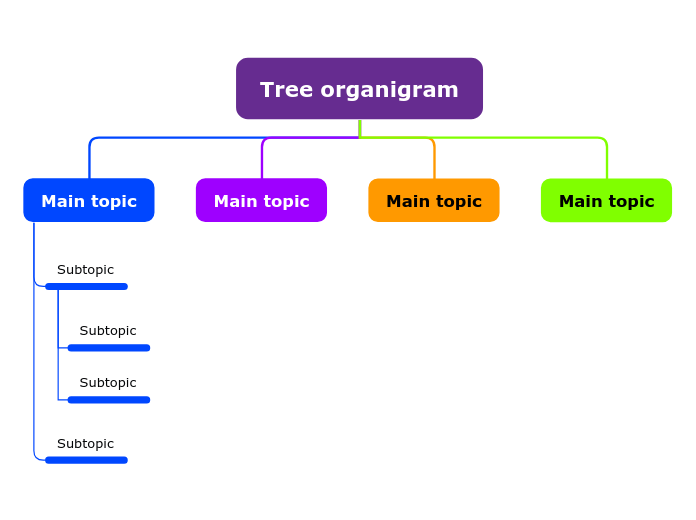
Image from:mindomo
4. Learning and Brainstorming:
Organize ideas, notes, and study materials.

Image from:Pinterest
There are various software options available to create tree maps, such as:、
- Mindmeister:Offers customizable templates and collaborative features.
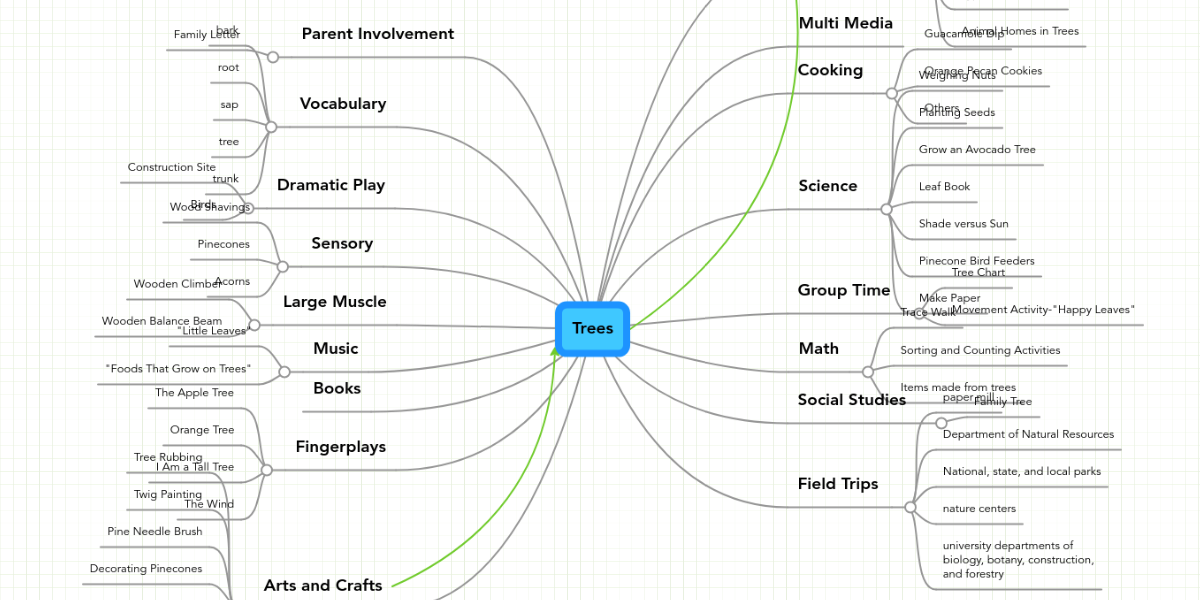
Image from:Mindmister
- XMind:Known for its flexibility and wide range of styling options.

Image from:Xmind
- Lucidchart:Great for professional-looking diagrams with advanced features.

Image from:Lucidchart
Conclusion
Mastering the art of tree map design involves a mix of logical structuring, visual appeal, and attention to detail. By following these best practices, you can create tree mind maps that not only look great but also effectively convey complex information in an organized manner. Whether you’re planning a project, mapping out a decision tree, or simply brainstorming ideas, a well-designed tree map can be a powerful tool in your productivity toolkit.
Start applying these tips today to see the difference in how you visualize and manage information!





















.C5FiwSKU_Z2vm2yk.webp)