Visual tools like Mandala maps and circular mind maps have revolutionized the way we organize and visualize information. These tools facilitate understanding, enhance creativity, and improve retention by presenting data in structured yet visually appealing formats. While both Mandala maps and circular mind maps share some similarities, they differ significantly in their design, purpose, and application. This blog explores these differences, starting with a detailed explanation of each tool and then comparing their key features.
What is a Mandala Map?
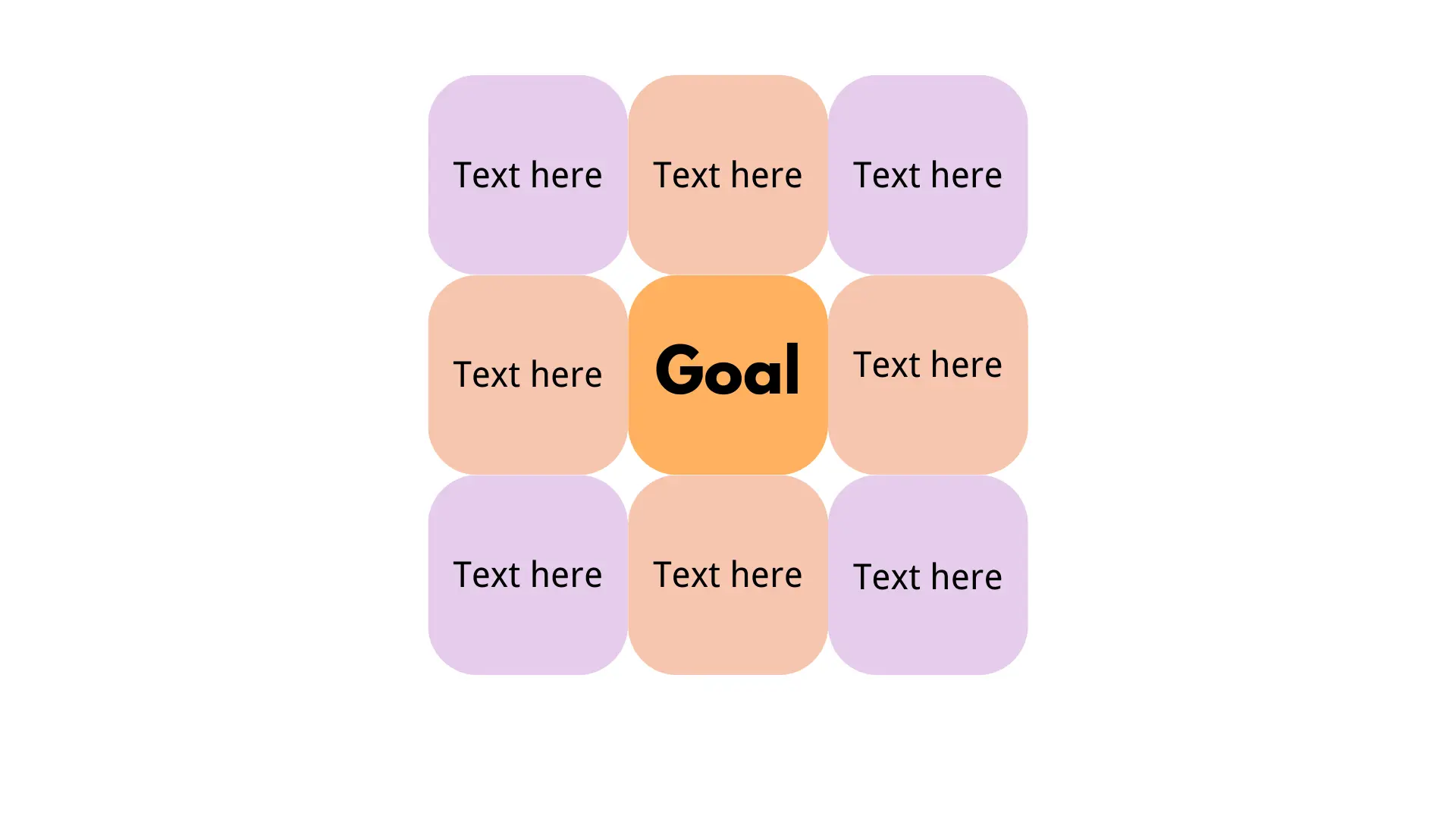
Let’s start with the definition of mandala map and circular mind map. A Mandala map, derived from traditional mandala designs, is a visually structured framework used for organizing and visualizing complex ideas, tasks, and goals. It features a central theme surrounded by related sub-categories, each further broken down into actionable items or smaller objectives. This multi-layered, concentric arrangement provides a holistic perspective, ensuring all aspects of a project or life goal are considered. Mandala maps integrate personal and professional development, offering a balanced approach to planning and problem-solving.
There are some key features of Mandala Maps.
1. Central Theme: The core idea or main goal is placed at the center of the map.
2. Concentric Layers: Ideas and tasks radiate outwards in layers, each representing different levels of detail or related sub-categories.
3. Visual Structure: Emphasizes symmetry and balance, often using colors and shapes for clarity and aesthetics.
4. Holistic Perspective: Ensures all aspects of a project or goal are considered, integrating both personal and professional development.
5. Actionable Items: Breaks down broader goals into smaller, manageable tasks.
With these various features, the main purposes of a Mandala map are to help in setting and planning goals by providing a clear structure and breaking down objectives into manageable tasks. It offers a holistic overview, ensuring all aspects related to the central theme are considered, promoting a balanced approach. By visually organizing related tasks and ideas, it enhances focus and aids in problem-solving by identifying interconnections. Additionally, it supports both personal and professional development by integrating growth aspects with professional objectives, fostering overall development.
What is a Circular Mind Map?
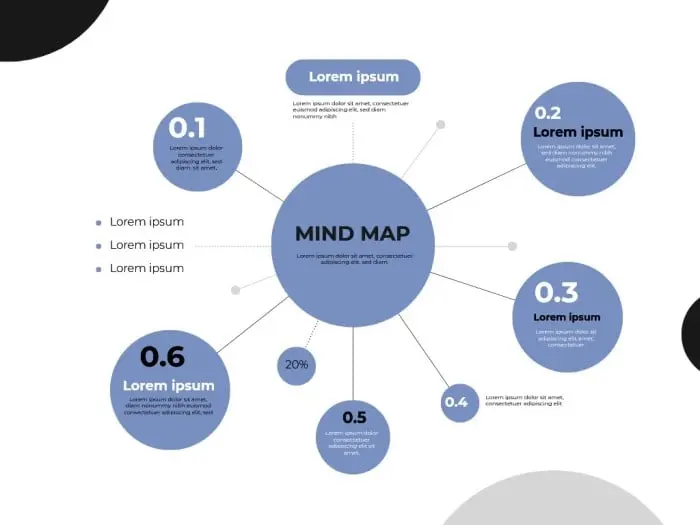
A circular mind map is a variant of the traditional mind map, which was popularized by Tony Buzan in the 1970s. Mind maps are brainstorming tools that help organize thoughts and ideas hierarchically. Circular mind maps retain the core principles of traditional mind maps but arrange information in a circular, rather than a tree-like, structure.
Key Features of Circular Mind Maps
1. Central Idea: The main idea or topic is placed at the center of the map.
2. Radial Layout: Ideas and sub-ideas radiate outwards from the central idea in a non-linear, circular pattern.
3. Hierarchy: Information is organized hierarchically, with main branches and sub-branches illustrating the relationships between ideas.
4. Flexibility: Allows for the addition of new branches and sub-branches as needed.
5. Visual Elements: Can include colors, images, and icons to differentiate between ideas and enhance the map’s visual appeal.
Although a circular mind map is comparable to a mandala map, the two have distinct applications. The following are some common purposes for which circular mind maps are used.
1. Brainstorming: Facilitates the generation and organization of ideas in a structured manner.
2. Note-Taking: Helps in capturing and organizing notes from lectures, meetings, or reading materials.
3. Project Planning: Assists in outlining project tasks, milestones, and timelines.
4. Problem-Solving: Helps in breaking down complex problems into manageable parts and identifying solutions.
5. Educational Purposes: Useful for summarizing and reviewing study materials.
What are their Differences?
While Mandala maps and circular mind maps are both powerful tools for visualizing and organizing information, they serve different purposes and have distinct features.
Visual Appeal
l Mandala Maps:
Mandala maps are designed with a focus on symmetry and balance, inspired by traditional mandala art. They emphasize visual harmony and aesthetics, often incorporating intricate patterns, colors, and shapes. This design enhances the meditative and reflective experience, making Mandala maps not just functional but also visually engaging.
l Circular Mind Maps:
Circular mind maps prioritize functionality and clarity over aesthetics. While they can still be visually appealing, their primary focus is on organizing information hierarchically and clearly. The design is typically simpler, using practical visual elements like colors, icons, and lines to differentiate between ideas and illustrate relationships.
Structure
l Mandala Maps:
Characterized by radial symmetry, Mandala maps feature ideas and tasks radiating outwards from a central theme in concentric layers. This structure ensures a balanced and holistic view, with more general ideas closer to the center and specific details further out. Each layer or ring represents different levels of detail or related sub-categories, creating a comprehensive and organized representation of information.
l Circular Mind Maps:
Circular mind maps also use a radial layout but emphasize hierarchical organization over symmetry. Ideas and sub-ideas radiate outwards from the central theme in a more flexible, non-linear pattern. The structure is less about visual balance and more about illustrating the relationships between main branches and sub-branches, helping users understand connections and dependencies.
Main Purpose
l Mandala Maps:
Often used for personal development, self-reflection, and creative projects, Mandala maps integrate both personal and professional aspects. They are ideal for goal setting, planning, and problem-solving, providing a balanced approach that considers all aspects of a project or life goal. The meditative process of creating a Mandala map can enhance mindfulness and personal growth.
l Circular Mind Maps:
Primarily used for brainstorming, note-taking, project planning, and educational purposes, circular mind maps are effective tools for organizing thoughts and ideas hierarchically. They facilitate the generation and organization of ideas, help capture and organize notes, outline project tasks and timelines, and break down complex problems into manageable parts. Their practical and structured design makes them ideal for summarizing and reviewing study materials.
Summary
Mandala maps and circular mind maps are both powerful visual tools for organizing and visualizing information. Mandala maps emphasize balance, symmetry, and aesthetics, making them ideal for personal development, project planning, and mindfulness practices. Circular mind maps prioritize hierarchical organization and functionality, making them suitable for brainstorming, note-taking, creative projects, and educational purposes.
By understanding the differences between these two tools, you can choose the one that best fits your needs and goals. Whether you are looking to enhance your personal growth, brainstorm creative ideas, or organize complex information, both Mandala maps and circular mind maps offer unique benefits that can help you achieve your objectives.




.DHf_86pa_fvIJu.webp)
