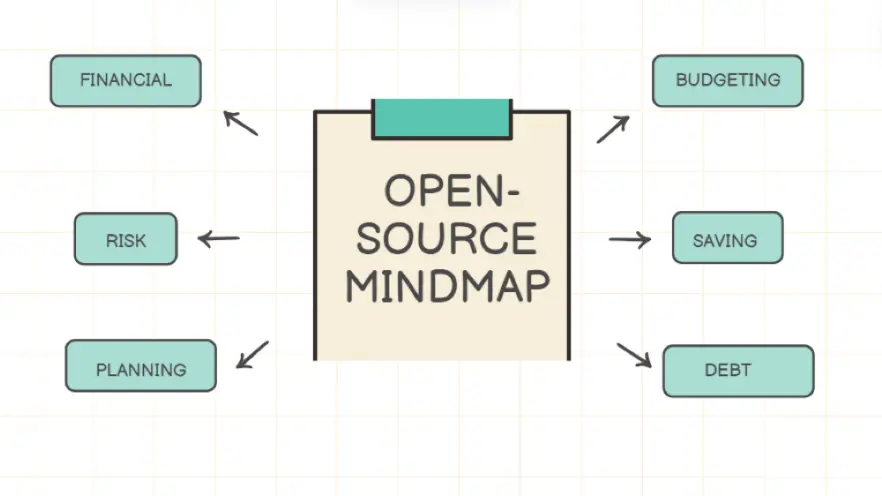
In the era of knowledge explosion, effective organization and management of information has become the key to enhancing cognitive efficiency and deep learning. Concept maps, as a visual knowledge representation tool, are becoming increasingly important. It is not only a means to promote the visualization of thinking, but also an important bridge to connect abstract concepts with concrete examples and build knowledge networks.
Concept map, as a knowledge visualization tool, is essentially a graphical representation of knowledge. Specifically, concept maps represent different concepts or entities through nodes, and utilize links or arrows to indicate the logical relationship or hierarchical structure between these concepts, thus forming an intuitive and systematic knowledge network. This representation not only reveals the intrinsic connection between concepts, but also promotes the integration and understanding of information.
Concept maps show unique advantages in organizing and expressing complex information. In the face of the complex ocean of information, concept maps can help us to pull out the silk from the cocoon, link the scattered knowledge points together, and form a well-organized and logical knowledge system. Through the construction of concept maps, we can understand the problem more systematically, grasp the essence and core of the problem, so as to make more accurate and comprehensive judgment and decision-making.

Image from: An integration of Mind Mapping and Concept Mapping (visual-mapping.com)
2.Why is there a need to build comprehensive concept maps?
In the context of a knowledge-intensive society, building comprehensive concept maps has become an efficient knowledge management and learning strategy. A comprehensive concept map is not only a simple listing of single knowledge points or concepts, but is committed to building a cross-domain, multi-level and interrelated knowledge network. Its necessity is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Improve comprehension
First, comprehensive concept mapping can significantly improve comprehension. By systematically organizing and presenting complex information, comprehensive concept mapping helps learners build a clear and coherent knowledge framework in their minds. This framed representation of knowledge helps learners to deeply understand the intrinsic connection and logical relationship between concepts, and thus grasp the overall structure and core points of knowledge.
Enhance memory
Secondly, the comprehensive concept map has a positive effect on enhancing memory. According to the theory of cognitive psychology, the more organized the information is, the easier it is to be encoded and stored by the memory system. By integrating and associating knowledge from different fields, the comprehensive concept map forms a highly organized knowledge network, and this networked representation of knowledge helps to reduce the burden of memory, improve the efficiency of memory, and promote the formation of long-term memory.
Improve communication skills
Furthermore, comprehensive concept mapping has significant advantages in improving communication skills. In academic exchanges, teamwork or project presentations, comprehensive concept maps can be used as an intuitive and concise communication tool to help participants quickly understand the essence and core of complex problems. Through sharing and discussing concept maps, individuals with different backgrounds and expertise can more easily reach a consensus and promote knowledge sharing and innovation.
A key role in different fields
Finally, comprehensive concept maps play a key role in integrating and correlating knowledge from different fields. In today’s increasingly interdisciplinary research, how to effectively integrate and correlate knowledge from different fields has become an important challenge for researchers. Comprehensive concept mapping breaks down the disciplinary barriers and promotes the cross-fertilization and innovative development of knowledge by constructing a cross-disciplinary knowledge network. This cross-field knowledge integration ability is of great significance for cultivating compound talents and promoting scientific and technological innovation.

Image from: Drawing On Math Concept Maps - vrogue.co
3.Steps in Building a Comprehensive Concept Map
In constructing a comprehensive concept map, it is critical to follow a series of systematic steps to ensure the completeness and validity of the final product. The following are the detailed steps in constructing a comprehensive concept map:
Step 1: Identify Themes
Selecting and clarifying the theme: first, the theme or central topic of the concept map needs to be clarified. This step requires the researcher or learner to have a clear goal orientation and to identify a representative topic that is worth exploring in depth based on research interests, learning needs, or program requirements.
Determining the scope of the theme: After the theme has been identified, its scope needs to be further defined. This includes identifying the key areas, core concepts, and possible boundary conditions covered by the theme. By narrowing or broadening the scope of the theme, the relevance and comprehensiveness of the concept map can be ensured. For example, a “problem decomposition” approach can be used to refine a complex theme into a series of sub-problems, thus gradually clarifying the specific scope of the theme.
Information sources: In order to build a comprehensive concept map, it is necessary to collect relevant information from a variety of sources. These include, but are not limited to, academic books, journal articles, online databases, web resources, and expert interviews. Diverse sources of information help ensure the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the concept map.
Organize and filter information: The information collected is often large and disorganized, and needs to be systematically organized and filtered. The information can be preliminarily processed through classification, summarization, comparison and other methods, eliminating irrelevant or repetitive content and retaining information that is closely related to the topic and of high quality. In addition, you can also use the “keyword extraction method” or “topic sentence extraction method” and other methods to refine the core concepts and key points in the information.

Image from: PNO is not asleep, just gathering information. – Panama Now Online
Step 3: Identify primary and secondary concepts
Distinguish between major and minor concepts: In the organized information, it is necessary to further identify the main concepts and minor concepts. Primary concepts are the key elements that form the core framework of the concept map, while secondary concepts complement or explain the primary concepts. Distinguishing between these two types of concepts helps to clarify the hierarchical structure and logical relationships of the concept map.
Methods of identifying concepts: In order to accurately identify concepts, a variety of methods can be used. For example, the “keyword method” identifies core concepts by extracting high-frequency words from the information; the “question method” guides the process of identifying concepts by asking a series of questions related to the topic. In addition, personal experience, professional knowledge, and literature review can be combined to make a comprehensive judgment.
Step 4: Establishing Conceptual Connections
Determine conceptual relationships: After identifying the primary and secondary concepts, links between them need to be established. These connections can be hierarchical relationships (e.g., inclusion and inclusion relationships), causal relationships (e.g., cause and effect relationships), similar relationships (e.g., associations between similar concepts), and so on. By clarifying the relationships between concepts, a well-organized and logical conceptual network can be constructed.
Techniques for establishing connections: In order to visualize the connections between concepts, graphical elements such as connecting lines and arrows can be used to connect different concept nodes. Also, different colors, line thicknesses, or marking symbols can be used to distinguish different types of connections. These techniques help to enhance the readability and expressiveness of the concept map.
Step 5: Optimize and beautify the concept map
Enhance readability and attractiveness: After completing the initial construction of the concept map, optimization and beautification work is required. This includes adjusting the layout, colors, fonts, and other elements to enhance the readability and appeal of the concept map. A reasonable layout helps to show the hierarchical and logical relationships between concepts; appropriate color combinations can highlight key information and enhance the visual effect; and clear fonts can help readers access information quickly and accurately.
Optimization suggestions: When optimizing and beautifying concept maps, some basic principles and suggestions can be followed. For example, keep the overall style consistent; highlight the main concepts and important connections; avoid too much redundant information and cluttered layout. In addition, concept maps can be customized according to specific needs, such as adding notes, charts or links to enhance their practicality and functionality.
Key points and tips in analyzing examples
Clarify the topic and scope: It is crucial to clarify the topic and its scope before building the concept map. This helps keep the concept map focused and relevant.
Gather and filter information from a wide range of sources: Comprehensive and accurate information from multiple sources is the foundation of a high-quality concept map. At the same time, a reasonable screening mechanism can ensure the effectiveness and conciseness of the information.
Accurate identification of concepts: Using scientific methods to accurately identify major and minor concepts is a key step in constructing a concept map. This helps to ensure the completeness and logic of the concept map.
Focus on optimization and beautification: Optimizing and beautifying the concept map can not only enhance its readability and attractiveness, but also enhance its practicality and persuasiveness. Therefore, attention should be paid to the details and overall layout in the construction process.
Practice is the only criterion to test the truth, and it is also the key way to improve personal ability. Therefore, we strongly encourage readers to put what they have learned into practice and build their own concept maps. Through continuous experimentation and reflection, readers can not only deepen their understanding of the concept map construction method, but also find new problems and put forward new insights in practice, thus promoting the innovation and development of knowledge.