
Step-by-Step Guide to Tree Mapping: Organize Your Thoughts and Information Visually
Tree mind map, as a central theme as the core, radiate outward branching, helping us in the learning journey to ride the waves.
Education Consultant


Image Source: pexels
Mind maps are effective tools for visually organizing thoughts and ideas. Each mind map begins with a central concept and branches out into related subtopics. This structure aids in brainstorming, project planning, and enhancing memory retention by 10-15%.
Flowcharts, on the other hand, depict processes through sequential steps, using symbols and arrows to illustrate the flow of actions. They excel in simplifying complex procedures and improving comprehension.
Combining flowcharts with mind maps can boost productivity by 23%. This integration leverages the strengths of both tools, creating a powerful method for visualizing information and processes. By combining flowcharts, you can enhance the clarity and efficiency of your visual representations.
Mind maps use nodes to represent ideas or concepts. Each node connects to other related nodes through lines. This structure helps visualize relationships between different pieces of information. Nodes often contain keywords or short phrases, making them easy to scan and understand. Connections between nodes show how ideas link together, creating a web of information.
Mind maps follow a hierarchical structure. The central concept sits at the core, with main branches extending outward. Each branch represents a major subtopic. Sub-branches break down these subtopics into finer details. This hierarchy helps organize information logically. It also aids in breaking down complex topics into manageable parts. Studies have shown that mind mapping improves the quality, structure, and coherence of written work.
Flowcharts use standardized symbols to represent different types of actions or decisions. Common symbols include rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions, and ovals for start and end points. Arrows connect these symbols, showing the direction of the process flow. This visual language makes it easy to follow steps and understand procedures.
Flowcharts depict processes in a sequential manner. Each step follows logically from the previous one. This linear progression helps clarify complex procedures. By laying out each action in order, flowcharts make it easier to identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies. This clarity enhances comprehension and simplifies troubleshooting.
Combining flowcharts with mind maps can create a powerful tool for visualizing both hierarchical relationships and sequential processes. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of both methods, enhancing the clarity and efficiency of visual representations.
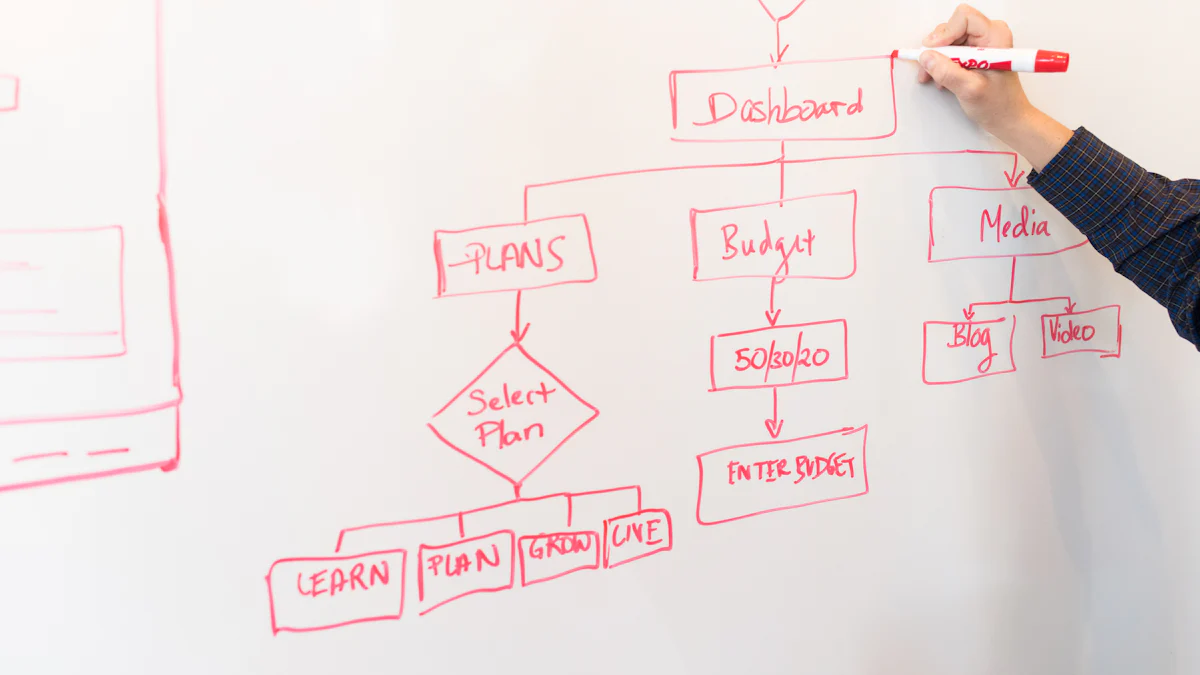
Image Source: pexels
Concept maps help visualize relationships between ideas. Each concept connects to another through labeled lines. This structure aids in understanding complex topics. Concept maps often use cross-links to show how different ideas relate. This method enhances comprehension by revealing hidden connections.
Spider maps, also known as spider diagrams, start with a central idea. Branches radiate outward to subtopics. Each subtopic can further break down into more detailed points. Spider maps excel in brainstorming sessions. The radial layout encourages free-flowing thought processes. This type of mind map helps in organizing ideas quickly and efficiently.
Overlaying flowcharts on mind maps combines hierarchical and sequential information. Start with a central topic in the mind map. Branch out into main subtopics. Use flowchart symbols within each branch to depict processes. Arrows can show the direction of actions. This hybrid approach provides a comprehensive view of both relationships and processes.
Incorporating flowchart symbols into mind maps enhances clarity. Use rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions, and ovals for start and end points. This method helps in visualizing steps within each subtopic. The combination of flowchart symbols with mind map nodes creates a versatile tool. This integration improves understanding and communication.
Combining flowcharts with mind maps offers several benefits. Embracing a mind map flowchart generator means integrating traditional benefits with modern digital conveniences. These generators facilitate capturing ideas seamlessly from the chaos of the brainstorming process and translating them into visual, organized, and interactive formats.
Increasing productivity doesn’t just mean moving faster. With mind maps, you can create and communicate ideas faster while operating with the same level of understanding. This combination helps increase your productivity and allows you to tackle more problems, brainstorm quickly, and communicate with confidence.

Image Source: pexels
Combining flowcharts with mind maps can enhance personal goal setting. A central node represents the main goal. Branches extend to sub-goals or milestones. Flowchart symbols illustrate the steps required to achieve each milestone. Arrows indicate the sequence of actions. This method provides a clear roadmap for achieving personal objectives.
Project planning benefits significantly from merging flowcharts and mind maps. Start with the project name as the central node. Main branches represent different phases of the project. Each phase breaks down into tasks using flowchart symbols. Arrows show task dependencies and sequences. This hybrid approach ensures comprehensive project visualization and efficient task management.
Educators can combine flowcharts with mind maps for effective lesson planning. The lesson topic serves as the central node. Main branches outline key concepts or sections of the lesson. Flowchart symbols within each branch detail instructional steps and activities. Arrows guide the flow of the lesson. This method enhances lesson structure and delivery.
Students can use merged mind maps and flowcharts for project work. The project topic becomes the central node. Main branches represent major sections or components of the project. Flowchart symbols detail specific tasks or research steps. Arrows show the sequence of activities. This approach helps students organize their work and improve project outcomes.
Historical Examples:
Tony Buzan popularized the concept of mind maps in the 1970s. His work demonstrated the effectiveness of visualizing information hierarchically.
Ramon Llull, a medieval philosopher, used techniques similar to mind maps to present data. His methods laid the groundwork for modern mind mapping.
Porphyry of Tyros created one of the earliest examples of visually presenting information in the 3rd Century. His work on Aristotle’s Categories highlighted the power of visual aids in understanding complex concepts.
Combining flowcharts with mind maps leverages these historical techniques. This integration creates powerful tools for visualizing both hierarchical relationships and sequential processes.
Creating a mind map involves several key steps. Start by selecting a central concept or topic. Place this concept in the center of your workspace. Use tools like SimpleMind or XMind to facilitate this process.
SmartDraw offers features for brainstorming and planning. This tool supports the creation of elaborate diagrams that display information visually.
Integrating flowchart elements into your mind map enhances clarity and functionality. Follow these steps to combine flowcharts with your mind map:
ZenFlowchart and MindMeister provide robust platforms for creating combined diagrams. These tools support collaboration, allowing team members to contribute and refine the visual representation.
Combining flowcharts with mind maps creates a versatile tool for various applications. This approach leverages the strengths of both methods, enhancing the clarity and efficiency of visual representations.
Recapping the key points, merging flowcharts and mind maps enhances both hierarchical and sequential visualization. This hybrid approach boosts productivity and comprehension.
For effective use, follow these tips:
Experimentation and adaptation are crucial. Each project may require unique adjustments. Embrace flexibility to maximize the benefits of this powerful combination.

Tree mind map, as a central theme as the core, radiate outward branching, helping us in the learning journey to ride the waves.
Education Consultant
.Dms6sGst_ulvKc.webp)
In today's fast-paced and information-overload world, the ability to visualize and communicate complex ideas, processes, and strategies is paramount. Flowcharts and mind maps have emerged as powerful tools that help us tame the chaos and bring clarity to our thoughts.
Education Consultant

A step-by-step guide to effectively brainstorming with mindmaps.
Education Consultant