
Step-by-Step Guide to Merging Flowcharts and Mind Maps
Master the art of merging flowcharts and mind maps with our step-by-step guide. Enhance your project planning and goal setting with integrated visuals.
Education Consultant

Sailing in the ocean of information, having an efficient and systematic study notes is a valuable asset for every one of us learners. Tree mind map, as a central theme as the core, radiate outward branching, layer by layer refinement of the notes method, is with its unique non-linear structure and strong organizational capacity, to help us in the learning journey to ride the waves. It not only breaks the boundaries of traditional linear notes and stimulates our creative thinking, but also promotes comprehensive integration and deep understanding of knowledge. Next, let’s explore how Tree Mind Mapping can help us create better study notes and make learning more efficient and fun.
In the vast landscape of information and knowledge, navigating through complex ideas and interconnected concepts can often feel like wandering through a dense forest without a compass. This is where the art of Tree Mapping emerges as a beacon of clarity, illuminating the intricate pathways that lead to deeper understanding and innovation. Today, we embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries of Tree Mapping, exploring why it’s not just a tool but a vital skill for anyone seeking to make sense of the world and contribute meaningfully to it.
Tree Mapping, at its core, is a visual representation technique that mimics the branching structure of trees. It allows individuals and teams to capture, organize, and analyze information in a hierarchical and intuitive manner. Each branch represents a subtopic or a related idea, branching out from a central theme or problem statement. This structured approach not only simplifies complex information but also fosters creativity and collaboration by encouraging users to explore new connections and perspectives.
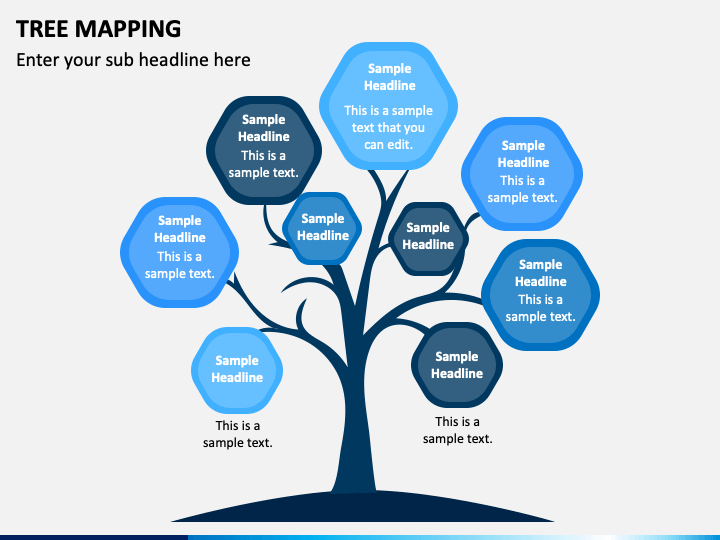
Image from: Tree Mapping PowerPoint and Google Slides Template - PPT Slides (sketchbubble.com)
In an era where information overload is the norm, Tree Mapping helps you sift through the noise and identify the most crucial elements of a topic. It ensures that your thoughts and ideas are well-structured and focused, making decision-making and problem-solving more efficient.
By visually mapping out ideas, Tree Mapping encourages lateral thinking and the exploration of unconventional solutions. It breaks down barriers between disciplines, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and the birth of innovative ideas.
Communicating complex concepts can be challenging, but Tree Mapping simplifies this process. Visual representations are easier to comprehend and share, ensuring that your message is received loud and clear by your audience.
In project management, Tree Mapping serves as a powerful tool for breaking down large tasks into manageable chunks, assigning responsibilities, and tracking progress. It keeps everyone on the same page and ensures that projects stay on track.
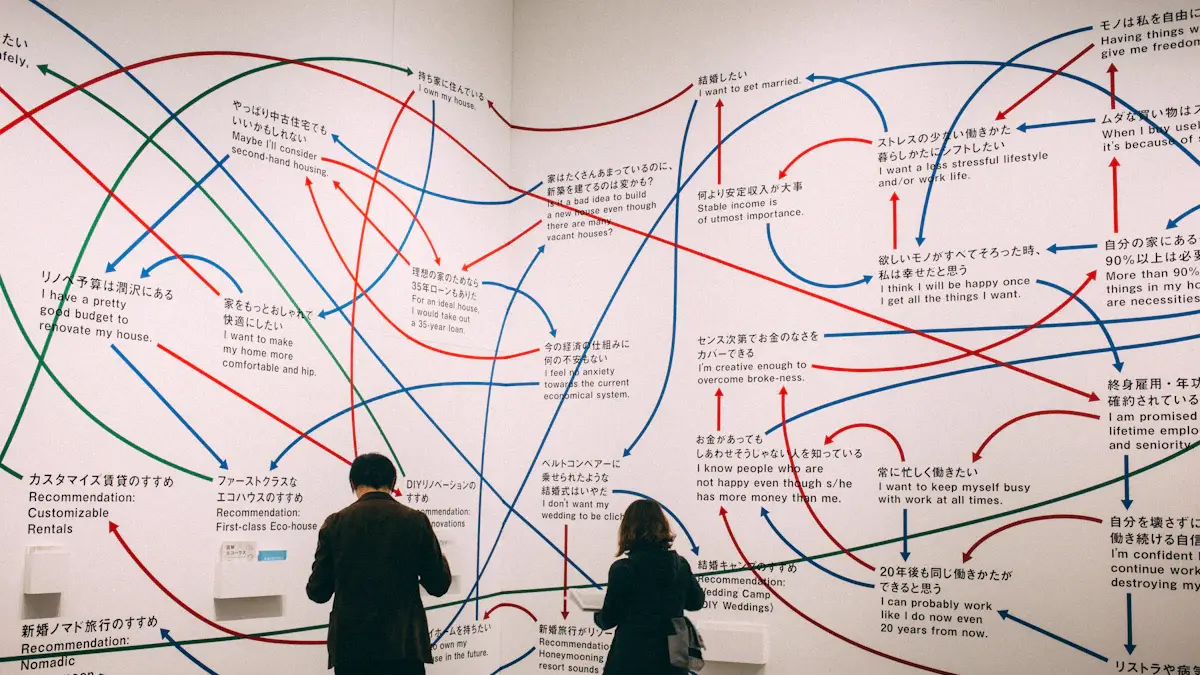
To truly ignite your interest in the transformative power of Tree Mapping, let’s delve into an inspiring example. Consider the development of the World Wide Web (WWW) by Sir Tim Berners-Lee. While working at CERN, Berners-Lee faced the challenge of organizing and sharing information among researchers from diverse backgrounds. Inspired by the concept of hypertext, he envisioned a global network of interconnected documents, which he famously sketched out on a whiteboard in the form of a tree structure. This simple yet revolutionary idea eventually evolved into the World Wide Web, revolutionizing the way we access, share, and create knowledge.
At the heart of Tree Mapping lies the elegant simplicity of its core principle—the tree-like structure. This natural metaphor mimics the branching patterns found in nature, where a trunk gives rise to branches, which further divide into twigs, ultimately supporting a vibrant ecosystem of leaves and fruit. Similarly, in the realm of information organization, the tree-like structure serves as a framework that systematically arranges data, ideas, and concepts into a clear and manageable hierarchy.
Each node in the tree represents a fundamental unit of information, whether it’s a topic, a subtopic, or a specific detail. These nodes are interconnected through branches, signifying relationships and dependencies. As you delve deeper into the tree, you uncover layers of increasingly specialized information, all rooted in a central idea or problem statement. This hierarchical organization not only facilitates comprehension but also encourages the discovery of patterns, connections, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Tree Mapping’s most striking advantage lies in its visual representation. By transforming abstract concepts into tangible, visual structures, it dramatically enhances comprehension and recall. The visual nature of Tree Mapping makes it easy for the brain to process and retain information.
By enforcing a hierarchical organization, Tree Mapping fosters structured thinking. It encourages users to break down complex issues into smaller, more manageable parts, ensuring that every idea has a logical place within the overall framework.
Despite its rigid appearance, the tree-like structure is incredibly flexible. It can accommodate new information and ideas seamlessly, allowing for continuous refinement and iteration. This adaptability makes Tree Mapping an ideal tool for dynamic environments where change is constant.
Tree Mapping is a collaborative art form. When used in group settings, it encourages open dialogue and shared understanding. Participants can build upon each other’s ideas, identify gaps in knowledge, and collaborate towards a common goal.
By visually mapping out information, Tree Mapping invites users to explore new connections and perspectives. It fosters a mindset of curiosity and experimentation, encouraging the generation of novel ideas and innovative solutions.
The first and crucial step in preparing for Tree Mapping is to clearly define the central theme or topic around which your tree will be constructed. This central idea serves as the trunk of your tree, providing the foundation and direction for all subsequent branches and sub-branches.
To select your topic, consider the following:
Relevance: Choose a topic that is relevant to your current project, research, or area of interest. This will ensure that your Tree Mapping exercise remains focused and purposeful.
Scope: Determine the scope of your topic. A broad topic may require a more extensive tree, while a narrow one can be mapped out more concisely.
Objectives: Identify your objectives for creating the Tree Mapping. Are you looking to organize information, brainstorm ideas, or visualize relationships? Your objectives will guide the structure and content of your tree.
Once you have chosen your topic, the next step is to gather the necessary information and materials. This involves researching, collecting, and organizing data that will populate your tree.
Research: Conduct thorough research to gather relevant information. Use books, articles, online resources, and interviews to build a comprehensive understanding of your topic.
Note-taking: As you research, take detailed notes. Highlight key points, make connections between ideas, and jot down any insights or questions that arise.
Organizing: Arrange your notes and information into logical categories or subtopics. This will help you visualize how the information will fit into your Tree Mapping.
When it comes to creating your Tree Mapping, you have two primary options: hand-drawn or software-based. Each has its own set of advantages and may be more suitable depending on your preferences, needs, and resources.
Hand-drawn Tree Mapping:
Advantages: It’s quick, easy, and requires no special equipment. It also allows for a more intuitive and spontaneous approach, as you can draw and revise your tree on the fly. Disadvantages: Hand-drawn trees can be difficult to share or collaborate on with others. They may also lack the precision and customization options offered by software.
Image from:A Guide to the Essential Eight Maturity Model: How to Apply it to Your Business? | Safetica
Software-based Tree Mapping:
Advantages: Software tools offer a wide range of customization options, including colors, shapes, and layouts. They also make it easy to share, collaborate, and revise your Tree Mapping with others. Additionally, software-based trees can be more visually appealing and professional-looking. Disadvantages: Some software tools can be expensive or require a learning curve. They may also be less intuitive than hand-drawn methods, especially for those who prefer a more tactile approach.
Image from:Mind Maps 05 PowerPoint Template (slideuplift.com)
Starting Point Establishment: Building the Foundation of Your Tree Mapping The root node is the central element of your Tree Mapping, representing the core topic or idea. It serves as the anchor from which all other branches and sub-branches will emanate.
Define Your Topic: Clearly state the main idea or focus of your Tree Mapping at the root node. This could be a question, a problem, or a central concept.
Make It Visible: Write or draw the root node prominently at the center of your page or canvas. Use a bold font or a distinct shape to make it stand out.
Branch Expansion: Radiating Wisdom from the Center From the root node, you will begin to add major branches that represent the primary categories or subtopics related to your central idea.
Identify Categories: Brainstorm and list all the main areas or aspects related to your topic. These will become your major branches.
Draw Branches: Starting from the root node, draw lines extending outwards to represent each major branch. Label each branch with its corresponding category or subtopic.
Organize Logically: Arrange the branches in a way that makes sense to you and your audience. You can use spatial positioning to imply relationships or importance.
Detail Exploration: Nurturing the Growth of Your Information Tree Under each major branch, you will add sub-branches to represent more specific details, ideas, or subcategories.
Break Down Further: For each major branch, think about the smaller, more specific aspects that belong to it. These will become your sub-branches.
Draw and Label: Extend lines from each major branch to create sub-branches, and label them accordingly. Continue this process as needed to add even more detailed sub-branches.
Maintain Clarity: Ensure that each sub-branch remains relevant to its parent branch and that the overall structure remains clear and easy to follow.
Optimization: Making Your Tree Mapping Both Practical and Aesthetically Pleasing Finally, take the time to organize and enhance your Tree Mapping to ensure it is both informative and visually appealing.
Reorganize: Review your Tree Mapping and rearrange branches or sub-branches if necessary to improve clarity and flow.
Use Colors and Shapes: Add color coding or different shapes to distinguish between different types of information or to highlight important points.
Edit and Refine: Check for typos, spelling errors, or any other inaccuracies. Ensure that all labels are clear and concise.
Add Annotations: If needed, add additional notes or explanations alongside branches or sub-branches to provide more context or clarification.
Finalize Layout: Consider the overall layout and make any final adjustments to ensure your Tree Mapping looks professional and inviting.
By following these 4 steps, you can create a comprehensive and visually appealing Tree Mapping that effectively organizes and communicates your ideas.
After the above introduction, I believe you have a general understanding of tree mind mapping, now put the theory into practice!

Master the art of merging flowcharts and mind maps with our step-by-step guide. Enhance your project planning and goal setting with integrated visuals.
Education Consultant

A step-by-step guide to effectively brainstorming with mindmaps.
Education Consultant
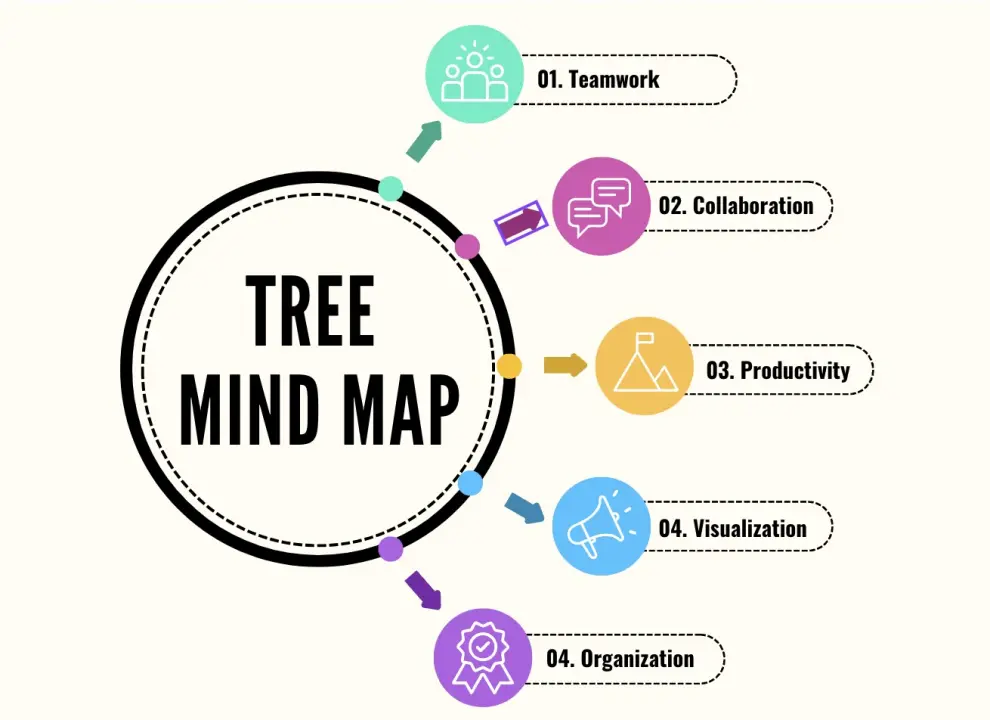
This blog post explores seven creative tree map examples that showcase the versatility and power of this data visualization technique.
Education Consultant