Mastering a new language can be a challenging yet rewarding journey. One of the most critical components of language learning is memory. How effectively you can retain and recall vocabulary, grammar rules, and phrases significantly impacts your progress. In this blog, we will explore how memory techniques mind maps can serve as a powerful tool for enhancing memory and facilitating language learning.
What are Memory Techniques Mind Maps?

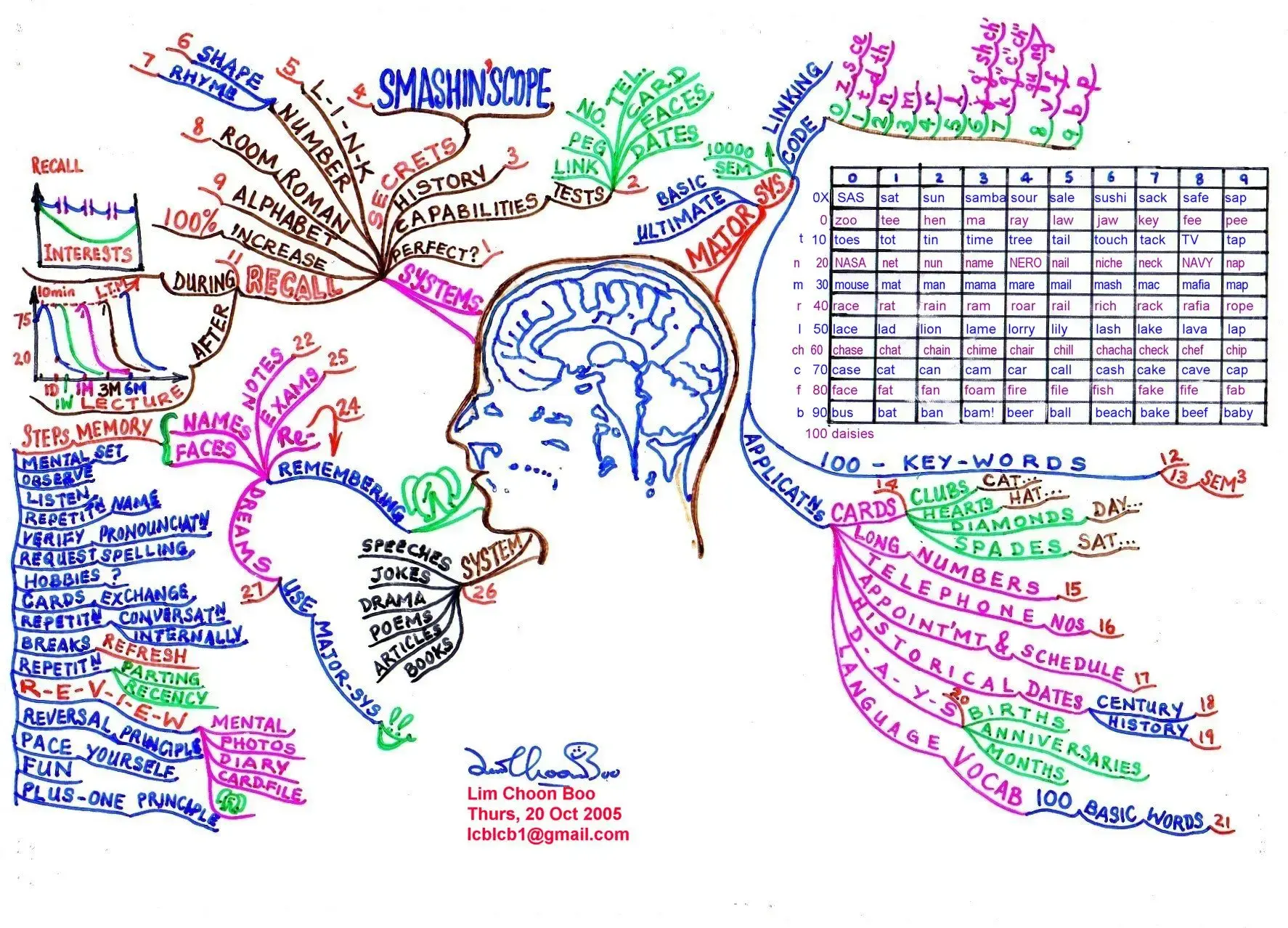
Image from: Linkedin
Memory techniques mind maps are visual representations of information that help learners organize and connect concepts. A mind map typically features a central topic at the center, with branches extending outward to related keywords, phrases, or images. This structure aligns with the brain’s natural way of processing information, making it easier to understand and remember complex subjects.
Benefits of Memory Techniques Mind Maps in Language Learning
- Improved Memory Retention: The combination of visual elements and structured information enhances your ability to retain and recall vocabulary and grammar.
- Enhanced Understanding: Memory techniques mind maps allow learners to see relationships between words and concepts, deepening their understanding.
- Organized Learning: By breaking down information into manageable parts, mind maps provide a clear overview of complex topics, making it easier to navigate and review.
- Engaging Process: Creating mind maps requires active participation, which boosts focus and retention. The use of colors and images makes learning more enjoyable.
- Adaptability: Memory techniques mind maps can be tailored to different learning styles, catering to visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners.
Memory Techniques to Combine with Mind Maps
1. Method of Loci (Memory Palace)

Image from: The 2-step “loci method” for memorizing absolutely anything - Big Think
- Assign vocabulary words or grammar rules to specific locations in a familiar mental space, such as your home or a journey you often take.
- Visualize placing the information in those locations, creating strong mental associations. For example, picture placing the word “bus” on your front doorstep, “train” inside your living room, and “taxi” in your kitchen.
- When recalling the words, mentally walk through your palace and retrieve the information from each location.
2. Mnemonics

Image from: literaryterms
- Create acronyms, rhymes, or phrases to remember vocabulary or grammar rules.
- Incorporate these mnemonics into the branches of your mind map for easy recall. For instance, to remember the prepositions “in, on, at,” you could use the mnemonic “I’m on a train.”
- Use the first letter of each word in the mnemonic to trigger the actual words.
3. Chunking

Image from: scribd
- Break down complex information into smaller, manageable parts.
- Organize these chunks into the branches and sub-branches of your mind map for clarity. For example, when learning verb tenses, create separate branches for “Present,” “Past,” and “Future,” with sub-branches for regular and irregular verbs.
- Group related words or grammar rules together to facilitate easier recall.
4. Spaced Repetition
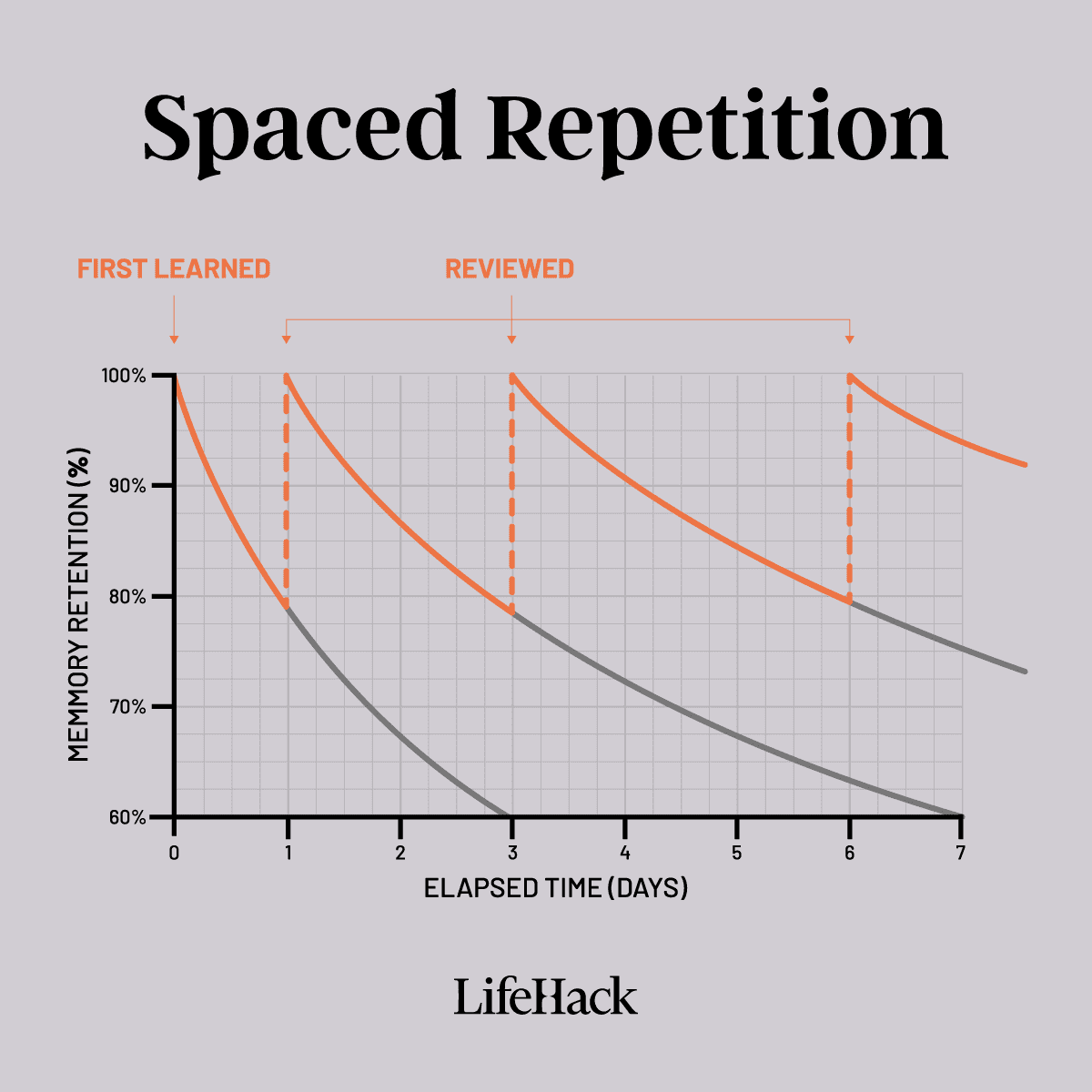
Image from: lifehack
- Review your mind map at increasing intervals over time (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly).
- Update the map with new vocabulary or grammar rules as you learn them to reinforce retention.
- Set reminders to review your mind map consistently, gradually increasing the time between reviews as the information becomes more ingrained.
How to Use Memory Techniques Mind Maps to Memorize Vocabulary
Using memory techniques mind maps to memorize vocabulary can transform the way you learn and retain new words. Here’s a detailed approach:

Image from: meistertask
1. Centralize Vocabulary
- Choose a Central Theme: Start with a central word or theme, such as “Food,” “Travel,” or “Nature.” Write this in the center of your mind map.
- Visual Appeal: Consider using a relevant image or icon in the center to make it visually engaging. This could be a drawing of a plate for “Food” or a suitcase for “Travel.”

Image from: meistertask
2. Branch Out
- Create Main Branches: Identify key categories related to your central theme. For example, under “Food,” you might have branches for “Fruits,” “Vegetables,” “Dishes,” and “Desserts.”
- Draw lines from the central topic to these branches, ensuring they radiate outward.
- Sub-Branches for Specific Words: For each main branch, create sub-branches that list specific vocabulary words. For instance, under “Fruits,” you could include “apple,” “banana,” “orange,” etc.
- Use keywords or short phrases to keep the information concise and memorable.
3. Visual Associations
- Draw Images: Next to each word, draw a small image or symbol that represents it. For example, a banana for “banana” or a slice of cake for “cake.” This visual cue aids in recall because it creates a mental image associated with the word.
- Color Coding: Use different colors for each category. For example, use green for fruits, orange for vegetables, etc. This visual differentiation can help you remember the categories more easily.
4. Use Mnemonics
- Create Mnemonics: Develop acronyms, rhymes, or phrases that help you remember groups of related words. For example, for fruits, you might create a mnemonic like “BAG” to remember “Banana, Apple, Grape.”
- Link Words with Stories: You can also create a short story that includes all the words. For example, “The banana and apple went to a party with a grape.” This narrative technique can make the words more memorable.
5. Regular Review
- Spaced Repetition: Schedule regular reviews of your mind map. Start with daily reviews, then move to weekly and monthly reviews. This reinforces memory and helps transfer vocabulary to long-term memory.
- Active Recall: During reviews, try to recall the words without looking at the mind map. This active engagement strengthens your memory and retention.
6. Practice Using Vocabulary
- Incorporate Words into Sentences: Practice writing sentences using the new vocabulary. This helps solidify your understanding of how the words are used in context.
- Engage in Conversations: Use the vocabulary in speaking exercises, either with a language partner or through language learning apps. Practicing in real-life situations enhances retention.
How to Use Memory Techniques Mind Maps to Learn Grammar

Image from: meistertask
Learning grammar through memory techniques mind maps can make complex rules more digestible and easier to remember. Here’s how to effectively use this method:
1. Central Grammar Concept
- Choose a Central Topic: Start with a central grammar topic, such as “Verb Tenses.” Write this in the center of your mind map.
- Visual Representation: Consider adding an image that represents the concept, such as a clock for tenses, to help visualize the time aspect of verbs.
2. Create Main Branches
- Develop Branches for Each Tense: Create branches for each verb tense, such as “Present,” “Past,” and “Future.” Each branch will represent a different category of verb tense.
- Sub-Branches for Forms: Under each tense, create sub-branches for different forms, such as “Simple,” “Continuous,” and “Perfect.” This organization helps clarify the structure of each tense.
3. Illustrate Examples
- Write Example Sentences: Next to each tense and form, write example sentences that illustrate its use. For example, under “Present Simple,” you might write, “I eat breakfast every day.”
- Use Color Coding: Differentiate the tenses with colors. For instance, use blue for present tenses, red for past tenses, and green for future tenses. This visual cue can help reinforce the distinctions between them.
4. Visualize Rules
- Draw Symbols for Rules: Create symbols or icons that represent key grammar rules. For example, use an upward arrow for “future” to signify actions that will happen, and a downward arrow for “past” to indicate completed actions.
- Summarize Rules: Write concise summaries of the rules next to each tense. For example, “Present Simple: Subject + base form of the verb (+s for third person).“
- Group Related Rules: Under each tense, group related grammar rules together. For example, under “Present,” include rules for affirmative, negative, and interrogative forms. This organization makes it easier to see how different rules relate to each other.
- Create Visual Connections: Draw lines or arrows to connect related rules or forms. This helps visualize relationships and reinforces understanding.
6. Review and Practice
- Regularly Review the Mind Map: Schedule consistent reviews of your grammar mind map. Use spaced repetition to reinforce your understanding of the rules.
- Practice Using Grammar in Context: Write paragraphs or dialogues using the grammar rules you’ve learned. This practice helps solidify your understanding and application of the rules.
- Engage in Exercises: Use language learning apps or textbooks that offer grammar exercises. Apply what you’ve learned in your mind map to these exercises for practical reinforcement.
By following these detailed steps for both vocabulary and grammar, you can effectively use memory techniques mind maps to enhance your language learning experience. This approach not only makes learning more engaging but also helps you retain and apply what you’ve learned in real-life situations.
Conclusion
Incorporating memory techniques mind maps into your language learning process can significantly improve your ability to memorize and recall information. By combining visual organization with effective memory strategies, you can enhance your understanding of vocabulary, grammar, and cultural nuances. Start creating your own mind maps today, and unlock your language learning potential through consistent practice and engagement!